When it comes to electrical systems, ensuring the correct wire size for a 100 amp feeder is essential for safety and efficiency. A 100 amp feeder is often used to supply power to subpanels, detached garages, or other structures requiring significant electrical capacity. Choosing the right wire size is not just a matter of convenience—it’s a matter of safety. The wrong wire size can lead to overheating, electrical fires, or system failures. Understanding the nuances of wire sizing is critical for both DIY enthusiasts and professional electricians alike.
Electrical codes and standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), provide guidelines for selecting the appropriate wire gauge based on factors like the amperage, distance, and material of the wire. Copper and aluminum are the two most common materials used for feeder wires, and each has its own advantages and limitations. While copper offers better conductivity, aluminum is often more cost-effective. Knowing how these factors influence your choice can save you time, money, and potential hazards.
Additionally, the length of the wire run plays a significant role in determining the correct wire size. Longer runs require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop, which can affect the performance of electrical devices. By understanding these factors, you can ensure that your 100 amp feeder wire size is not only compliant with regulations but also optimized for your specific needs. Let’s explore the key considerations and answer common questions to help you make an informed decision.
Read also:Kevin Spacey Kids A Deep Dive Into His Life And Family Secrets
Table of Contents
- What is a 100 Amp Feeder?
- Why Does Wire Size Matter for a 100 Amp Feeder?
- How to Choose the Right Wire for a 100 Amp Feeder?
- Copper vs. Aluminum Wires: Which is Better for 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting a 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size
- Can You Use a Smaller Wire for a 100 Amp Feeder?
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop for a 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size?
- What Are the Legal Requirements for 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size?
- How to Install a 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size Safely?
- Frequently Asked Questions About 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size
What is a 100 Amp Feeder?
A 100 amp feeder is a dedicated electrical circuit designed to supply power from the main service panel to a subpanel or another structure. It is commonly used in residential and commercial settings where additional electrical capacity is needed. For example, a detached garage, workshop, or outbuilding may require a 100 amp feeder to support tools, lighting, and appliances. The feeder wire is the conductor that carries the electrical current from the main panel to the subpanel, and its size is critical to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Why Does Wire Size Matter for a 100 Amp Feeder?
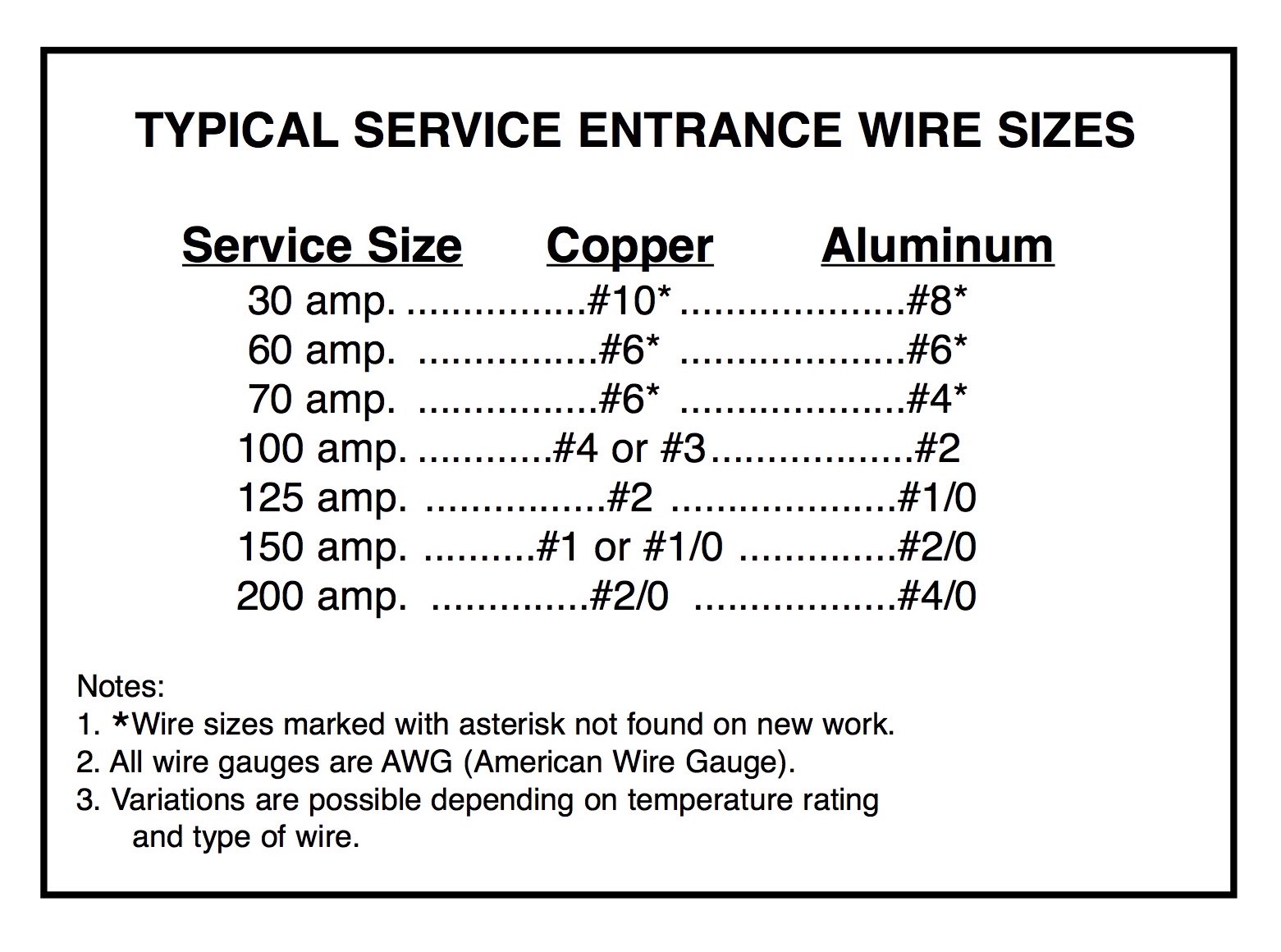
The size of the wire used for a 100 amp feeder directly impacts its ability to handle the electrical load safely. If the wire is too small, it can overheat, leading to insulation damage, fire hazards, or equipment failure. On the other hand, using a wire that is unnecessarily large can result in wasted materials and higher costs. The wire size is determined by factors such as the amperage, the material of the wire, and the length of the run. For a 100 amp feeder, the most common wire sizes are 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum, but these may vary depending on specific circumstances.
How to Choose the Right Wire for a 100 Amp Feeder?
Selecting the right wire for a 100 amp feeder involves several considerations. First, you need to determine the material of the wire—copper or aluminum. Copper is more conductive, meaning it can carry more current with a smaller diameter, while aluminum is lighter and less expensive. Next, consider the distance between the main panel and the subpanel. Longer distances require larger wire sizes to compensate for voltage drop. Finally, consult local electrical codes and regulations to ensure compliance. These steps will help you choose the correct 100 amp feeder wire size for your project.
Copper vs. Aluminum Wires: Which is Better for 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size?
When selecting a wire for a 100 amp feeder, the choice between copper and aluminum is a common dilemma. Copper wires are known for their superior conductivity, which allows them to carry more current with a smaller gauge. For example, a 2 AWG copper wire is typically sufficient for a 100 amp feeder. However, copper is more expensive than aluminum, making it less budget-friendly for larger projects.
Aluminum wires, on the other hand, are lighter and more affordable. A 1/0 AWG aluminum wire is often recommended for a 100 amp feeder. However, aluminum has lower conductivity, which means it requires a larger gauge to carry the same current as copper. Additionally, aluminum wires are more prone to oxidation, which can lead to connection issues over time. Proper installation techniques, such as using anti-oxidant compounds and compatible connectors, are essential when working with aluminum wires.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting a 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size
Making the wrong choice when selecting a 100 amp feeder wire size can lead to serious consequences. One common mistake is underestimating the wire size needed for the load. This can result in overheating and potential fire hazards. Another mistake is ignoring the length of the wire run, which can cause excessive voltage drop and reduce the performance of electrical devices.
Read also:Jenna Haze Unveiling The Journey Of An Iconic Personality
Using the wrong type of wire material or failing to follow local electrical codes are also frequent errors. Always consult a professional electrician or refer to the NEC guidelines to ensure compliance. By avoiding these mistakes, you can ensure that your 100 amp feeder wire size is both safe and efficient.
Can You Use a Smaller Wire for a 100 Amp Feeder?
Using a smaller wire for a 100 amp feeder is not recommended and can be dangerous. Smaller wires have higher resistance, which can lead to overheating and voltage drop. For example, a 4 AWG copper wire may seem sufficient, but it is not rated for 100 amps and could pose a fire risk. Always use the appropriate wire size based on the amperage and distance to ensure safety and compliance with electrical codes.
How to Calculate Voltage Drop for a 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size?
Voltage drop is an important consideration when selecting a 100 amp feeder wire size. It refers to the loss of voltage that occurs as electricity travels through a wire. Excessive voltage drop can cause appliances and equipment to underperform or malfunction. To calculate voltage drop, you need to know the wire’s resistance, the current, and the length of the wire run.
The formula for voltage drop is: Voltage Drop = (2 x Wire Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000. For a 100 amp feeder, a voltage drop of more than 3% is generally considered unacceptable. By using this formula, you can determine the appropriate wire size to minimize voltage drop and ensure optimal performance.
What Are the Legal Requirements for 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size?
Legal requirements for 100 amp feeder wire size are governed by the NEC and local building codes. These regulations specify the minimum wire size and material requirements for different amperages and applications. For example, the NEC requires that a 100 amp feeder use a minimum of 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum wire. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, penalties, or even the rejection of your electrical installation.
How to Install a 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size Safely?
Installing a 100 amp feeder wire size requires careful planning and execution. Start by turning off the main power supply to ensure safety. Then, measure the distance between the main panel and the subpanel to determine the appropriate wire size. Use conduit to protect the wire and ensure it is properly secured along its path.
When connecting the wires, ensure that all connections are tight and corrosion-free. Use anti-oxidant compounds for aluminum wires and ensure that the breaker and subpanel are rated for 100 amps. Finally, test the system to ensure it is functioning correctly before restoring power. If you’re unsure about any step, consult a licensed electrician.
Frequently Asked Questions About 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size
1. What is the minimum wire size for a 100 amp feeder?
The minimum wire size for a 100 amp feeder is 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum, as per NEC guidelines.
2. Can I use aluminum wire for a 100 amp feeder?
Yes, you can use aluminum wire for a 100 amp feeder, but it must be 1/0 AWG or larger to ensure safety and compliance.
3. How do I calculate voltage drop for a 100 amp feeder?
Use the formula: Voltage Drop = (2 x Wire Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000 to calculate voltage drop.
4. What are the consequences of using the wrong wire size?
Using the wrong wire size can lead to overheating, voltage drop, and potential fire hazards.
By understanding these key aspects of 100 amp feeder wire size, you can ensure a safe and efficient electrical installation. Always prioritize safety and compliance with regulations to avoid costly mistakes and hazards.