When it comes to electrical systems, safety and efficiency are paramount, and selecting the correct wire gauge for a 100 amp circuit is critical to ensuring both. Whether you're planning a new installation or upgrading an existing one, understanding the role of wire gauge is essential. The gauge of a wire determines its ability to carry electrical current safely without overheating or causing damage. For a 100 amp circuit, using the wrong wire gauge can lead to serious hazards, including electrical fires and system failures. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about choosing the right gauge wire for 100 amp applications.
Electrical systems are designed to handle specific loads, and the wire gauge you choose must align with the amperage of the circuit. For 100 amp circuits, the wire must be thick enough to handle the current without excessive resistance, which can cause overheating. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for wire sizing, but understanding these recommendations requires a deeper dive into factors like wire material, length of the run, and environmental conditions. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of how to select the right gauge wire for 100 amp circuits and why it matters.
Choosing the correct wire gauge is not just about compliance with codes; it's also about ensuring the longevity and reliability of your electrical system. A properly sized wire minimizes voltage drop, improves efficiency, and reduces the risk of electrical hazards. This article will explore the factors that influence wire gauge selection, common mistakes to avoid, and practical tips for installation. Whether you're a DIY enthusiast or a professional electrician, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about gauge wire for 100 amp circuits.
Read also:Best Free Web Ssh Access For Iot Devices On Raspberry Pi
- What Is Gauge Wire for 100 Amp?
- Why Does Wire Gauge Matter for 100 Amp?
- How to Choose the Right Gauge Wire for 100 Amp?
- What Are the Common Mistakes When Selecting Wire Gauge?
- Copper vs. Aluminum Wire for 100 Amp
- Factors Affecting Wire Gauge Selection
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop in a 100 Amp Circuit?
- Tools and Resources for Selecting Wire Gauge
- Best Practices for Installing 100 Amp Wiring
- Frequently Asked Questions About Gauge Wire for 100 Amp
What Is Gauge Wire for 100 Amp?
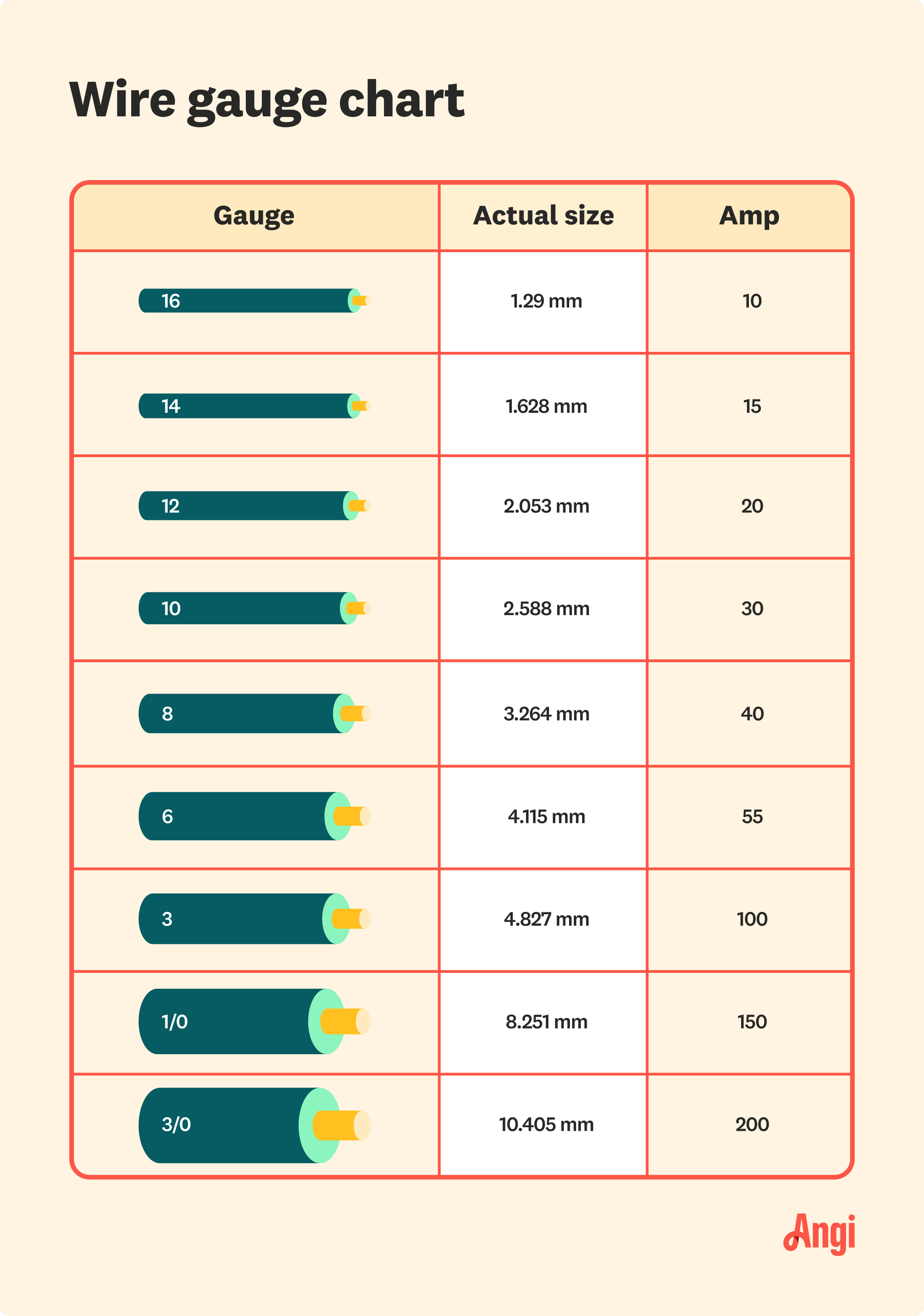
Gauge wire for 100 amp refers to the thickness of the wire used in electrical circuits designed to handle up to 100 amps of current. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system is used to standardize wire sizes, with lower gauge numbers indicating thicker wires. For a 100 amp circuit, the recommended wire gauge is typically 2 AWG for copper wires and 1/0 AWG for aluminum wires. These sizes are designed to safely carry the current without overheating or causing voltage drop issues.
Understanding the relationship between wire gauge and current capacity is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. Thicker wires have lower resistance, which allows them to carry more current without generating excessive heat. This is particularly important for high-amperage circuits like those used in residential and commercial electrical panels.
Why Does Wire Gauge Matter for 100 Amp?
Wire gauge matters for 100 amp circuits because it directly impacts the safety and performance of the electrical system. Using a wire that is too thin for the current load can lead to overheating, insulation damage, and even electrical fires. On the other hand, using a wire that is unnecessarily thick can increase costs and make installation more difficult.
The gauge of the wire also affects voltage drop, which is the reduction in voltage as electricity travels through the wire. Excessive voltage drop can cause appliances and equipment to operate inefficiently or fail altogether. By selecting the appropriate gauge wire for 100 amp circuits, you can minimize voltage drop and ensure reliable performance.
How to Choose the Right Gauge Wire for 100 Amp?
Choosing the right gauge wire for 100 amp involves considering several factors, including the material of the wire, the length of the run, and the environmental conditions. Copper wires are generally preferred for their superior conductivity, but aluminum wires are a cost-effective alternative for longer runs.
To determine the correct wire gauge, you can refer to the NEC guidelines or use an online wire size calculator. These tools take into account the amperage, voltage, and distance to provide a recommendation for the appropriate wire gauge. Additionally, it's important to consider local building codes and regulations, which may have specific requirements for wire sizing.
Read also:Who Is Apolo Ohnos Wife A Complete Guide To The Olympic Champions Life And Love
What Are the Common Mistakes When Selecting Wire Gauge?
One common mistake when selecting wire gauge for 100 amp circuits is underestimating the importance of voltage drop. Many people focus solely on the current capacity of the wire and overlook the impact of distance on voltage drop. This can result in inefficient performance and potential damage to connected devices.
Another mistake is using aluminum wire without accounting for its lower conductivity compared to copper. Aluminum wires require a larger gauge to carry the same current as copper wires, and failing to adjust for this difference can lead to overheating and safety hazards.
Copper vs. Aluminum Wire for 100 Amp
When it comes to gauge wire for 100 amp circuits, the choice between copper and aluminum is a critical decision. Copper wires are known for their excellent conductivity and durability, making them the preferred choice for most applications. However, they are more expensive than aluminum wires, which can be a consideration for larger projects.
Aluminum wires, while less conductive, are lighter and more cost-effective. They are often used in long-distance runs where weight and cost are significant factors. However, aluminum requires careful installation techniques to prevent issues like corrosion and loosening connections.
Factors Affecting Wire Gauge Selection
Several factors influence the selection of gauge wire for 100 amp circuits. These include the type of load being powered, the length of the wire run, and the ambient temperature. High-temperature environments may require larger wire gauges to compensate for increased resistance.
Other considerations include the type of insulation used on the wire and the presence of any additional protective measures, such as conduits or raceways. Proper planning and consultation with a qualified electrician can help ensure that all factors are taken into account.
How to Calculate Voltage Drop in a 100 Amp Circuit?
Calculating voltage drop in a 100 amp circuit involves using a formula that takes into account the wire's resistance, the current load, and the length of the run. The formula is: Voltage Drop = (2 x Wire Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000.
For example, if you're using a 2 AWG copper wire with a resistance of 0.194 ohms per 1,000 feet and the run is 100 feet long, the voltage drop would be approximately 3.88 volts. This calculation helps ensure that the voltage drop remains within acceptable limits, typically less than 3% for most applications.
Tools and Resources for Selecting Wire Gauge
There are several tools and resources available to help you select the correct gauge wire for 100 amp circuits. Online wire size calculators are a convenient option, allowing you to input the amperage, voltage, and distance to receive a recommendation.
Additionally, the NEC provides detailed tables and guidelines for wire sizing, which can be referenced for specific applications. Consulting with a licensed electrician or electrical engineer is also advisable for complex projects or situations where local codes may apply.
Best Practices for Installing 100 Amp Wiring
Installing gauge wire for 100 amp circuits requires careful planning and adherence to best practices. Properly sizing the wire, using the correct connectors, and ensuring secure connections are all critical steps in the installation process.
It's also important to follow safety guidelines, such as turning off the power before working on the circuit and using insulated tools. Regular inspections and maintenance can help identify and address potential issues before they become serious problems.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gauge Wire for 100 Amp
What gauge wire is needed for 100 amp service? For 100 amp service, a 2 AWG copper wire or 1/0 AWG aluminum wire is typically recommended.
Can I use a smaller gauge wire for a 100 amp circuit? Using a smaller gauge wire than recommended can lead to overheating and safety hazards, so it's important to follow guidelines.
How does temperature affect wire gauge selection? Higher temperatures can increase resistance, requiring larger wire gauges to compensate and maintain safe operation.
What tools can help me calculate wire size? Online wire size calculators and NEC tables are valuable resources for determining the appropriate wire gauge.
By understanding the importance of gauge wire for 100 amp circuits and following best practices, you can ensure a safe and efficient electrical system. This guide provides the knowledge and tools you need to make informed decisions and avoid common pitfalls.