Whether you're an electrician, a DIY enthusiast, or a homeowner, knowing the correct wire gauge for a 100-amp circuit ensures that your system operates safely and meets electrical code requirements.
When we talk about wire gauge, we refer to the thickness or diameter of the wire, which directly impacts its ability to carry current. For a 100-amp circuit, the wire gauge must be thick enough to handle the load while minimizing resistance and heat buildup. Copper and aluminum are the two most common materials used for electrical wiring, and each has different gauge requirements for the same amperage. Understanding these differences is key to selecting the right wire for your needs. This guide will delve into the specifics of wire gauges, materials, and factors to consider when determining what gauge is 100 amp wire.
In addition to safety, selecting the correct wire gauge also affects the performance and longevity of your electrical system. A wire that is too thin for the amperage it carries will degrade over time, leading to costly repairs and potential hazards. On the other hand, using a wire that is unnecessarily thick can increase costs without providing additional benefits. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the factors influencing wire gauge selection, answer common questions like "what gauge is 100 amp wire," and offer practical tips to help you make informed decisions for your electrical projects.
Read also:Mastering Aws Remoteiot Vpc Ssh Download Free A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- What is Wire Gauge?
- What Gauge is 100 Amp Wire?
- What Factors Affect Wire Gauge Selection?
- Copper vs. Aluminum Wire: Which is Better?
- How to Choose the Right Wire for 100 Amps?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire Gauge
- What Are the Risks of Using the Wrong Wire Gauge?
- How to Measure Wire Gauge?
- Why is Wire Gauge Important for Electrical Safety?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Gauge
What is Wire Gauge?
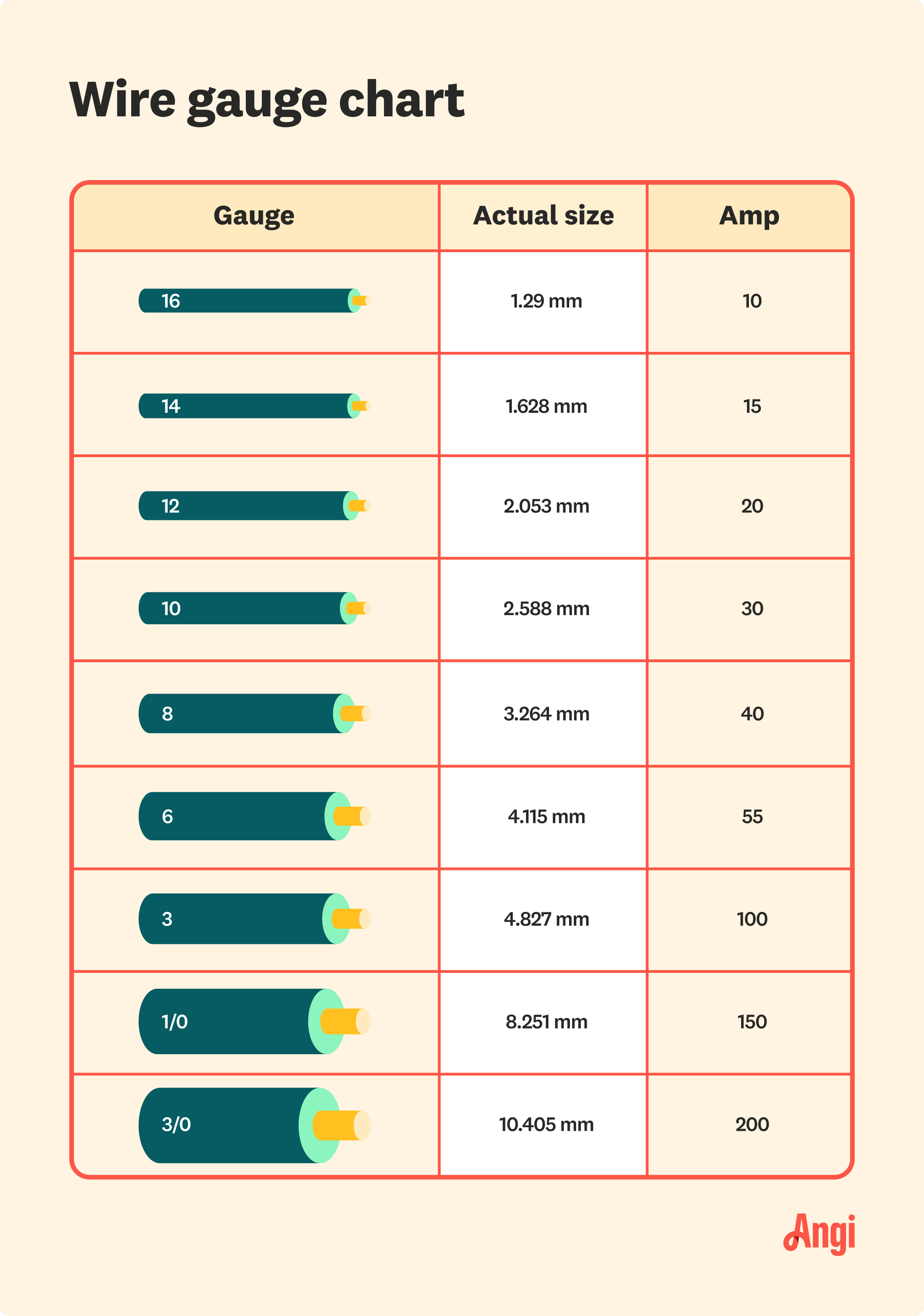
Wire gauge refers to the measurement of a wire's diameter, which determines its capacity to carry electrical current. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system is the standard used in the United States to classify wire sizes. In this system, a lower gauge number indicates a thicker wire, while a higher gauge number signifies a thinner wire. For example, a 1-gauge wire is much thicker than a 14-gauge wire. Understanding wire gauge is crucial for ensuring that the wire can handle the current load without overheating or causing electrical hazards.
What Gauge is 100 Amp Wire?
When it comes to a 100-amp circuit, the appropriate wire gauge depends on the material of the wire. For copper wires, a 3-gauge wire is typically recommended for 100 amps, while aluminum wires require a thicker 1-gauge wire due to their higher resistance. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for wire gauge selection based on amperage, distance, and material. These standards ensure that the wire can safely handle the load without overheating or causing electrical fires.
What Factors Affect Wire Gauge Selection?
Several factors influence the selection of the correct wire gauge for a 100-amp circuit. These include:
- The material of the wire (copper or aluminum).
- The length of the wire run, as longer distances require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop.
- The environment where the wire will be installed, such as temperature and exposure to moisture.
- Local electrical codes and regulations.
Copper vs. Aluminum Wire: Which is Better?
Both copper and aluminum are commonly used for electrical wiring, but they have distinct differences that affect their performance. Copper is more conductive and durable, making it ideal for most applications. However, it is also more expensive. Aluminum, on the other hand, is lighter and more affordable but has higher resistance, requiring a thicker gauge for the same amperage. Understanding these differences is essential when determining what gauge is 100 amp wire.
How to Choose the Right Wire for 100 Amps?
Selecting the right wire for a 100-amp circuit involves evaluating several factors, including the type of material, the length of the wire run, and the specific requirements of your project. Here are some steps to guide you:
- Check the NEC guidelines for wire gauge recommendations.
- Consider the distance between the power source and the load.
- Evaluate the environment where the wire will be installed.
- Consult a licensed electrician for professional advice.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire Gauge
Choosing the wrong wire gauge can lead to serious consequences. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Read also:Anissa Jones The Life And Legacy Of A Child Star
- Using a wire that is too thin for the amperage it needs to carry.
- Ignoring the impact of wire length on voltage drop.
- Overlooking local electrical codes and regulations.
- Selecting the wrong material for the application.
What Are the Risks of Using the Wrong Wire Gauge?
Using the wrong wire gauge for a 100-amp circuit can result in overheating, electrical fires, and equipment damage. It can also lead to voltage drop, which affects the performance of electrical devices. Understanding what gauge is 100 amp wire is essential to avoid these risks and ensure the safety and efficiency of your electrical system.
How to Measure Wire Gauge?
Measuring wire gauge accurately is important for ensuring that the wire meets the requirements of your project. You can use a wire gauge tool or consult a wire gauge chart to determine the thickness of the wire. Always verify the gauge before installation to ensure compliance with electrical codes.
Why is Wire Gauge Important for Electrical Safety?
Wire gauge plays a critical role in electrical safety by ensuring that the wire can handle the current load without overheating. Using the correct wire gauge reduces the risk of electrical fires, equipment failure, and other hazards. This is especially important for high-amperage circuits like 100 amps, where the stakes are higher.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Gauge
Here are some common questions about wire gauge and their answers:
What is the Difference Between Copper and Aluminum Wire?
Copper is more conductive and durable, while aluminum is lighter and more affordable. However, aluminum requires a thicker gauge for the same amperage due to its higher resistance.
How Do I Know If My Wire is the Right Gauge?
You can check the wire's gauge using a wire gauge tool or consult a wire gauge chart. Always refer to the NEC guidelines and local electrical codes for confirmation.
What Gauge is 100 Amp Wire for Long Distances?
For long distances, you may need to use a thicker wire to minimize voltage drop. Consult an electrician to determine the appropriate gauge based on the length of the wire run.
Can I Use a Thicker Wire Than Recommended?
Yes, using a thicker wire than recommended is safe and can improve performance. However, it may increase costs without providing significant benefits for short distances.
Understanding what gauge is 100 amp wire is essential for anyone working on electrical projects. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can ensure that your system operates safely and efficiently while meeting all necessary requirements.