Choosing the right wire size for a 100-amp electrical service is crucial for safety, efficiency, and compliance with electrical codes. Many homeowners and DIY enthusiasts often find themselves asking, "What size is 100 amp wire?" because the answer can vary based on factors like distance, material type, and installation conditions. Using the wrong wire size can lead to overheating, voltage drop, or even fire hazards. Understanding the correct specifications ensures that your electrical system operates reliably and safely.
When planning an electrical project, it's essential to know the specific requirements for a 100-amp wire. The wire gauge is determined by the amount of current it needs to carry, as well as the distance it must travel. Copper and aluminum are the two most common materials used for wiring, and each has its own advantages and limitations. Copper wires are more conductive and durable but come at a higher cost, while aluminum wires are more affordable but require larger gauges to handle the same current load.
Electrical codes and regulations, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), provide guidelines for selecting the appropriate wire size for a 100-amp service. These standards ensure that installations are safe and meet industry best practices. Whether you're installing a new breaker panel, upgrading your service, or wiring a subpanel, knowing what size is 100 amp wire is the first step toward a successful project. Let’s dive deeper into the factors that influence wire size and how to make the best choice for your needs.
Read also:Anissa Jones The Life And Legacy Of A Child Star
Table of Contents
What Size is 100 Amp Wire?
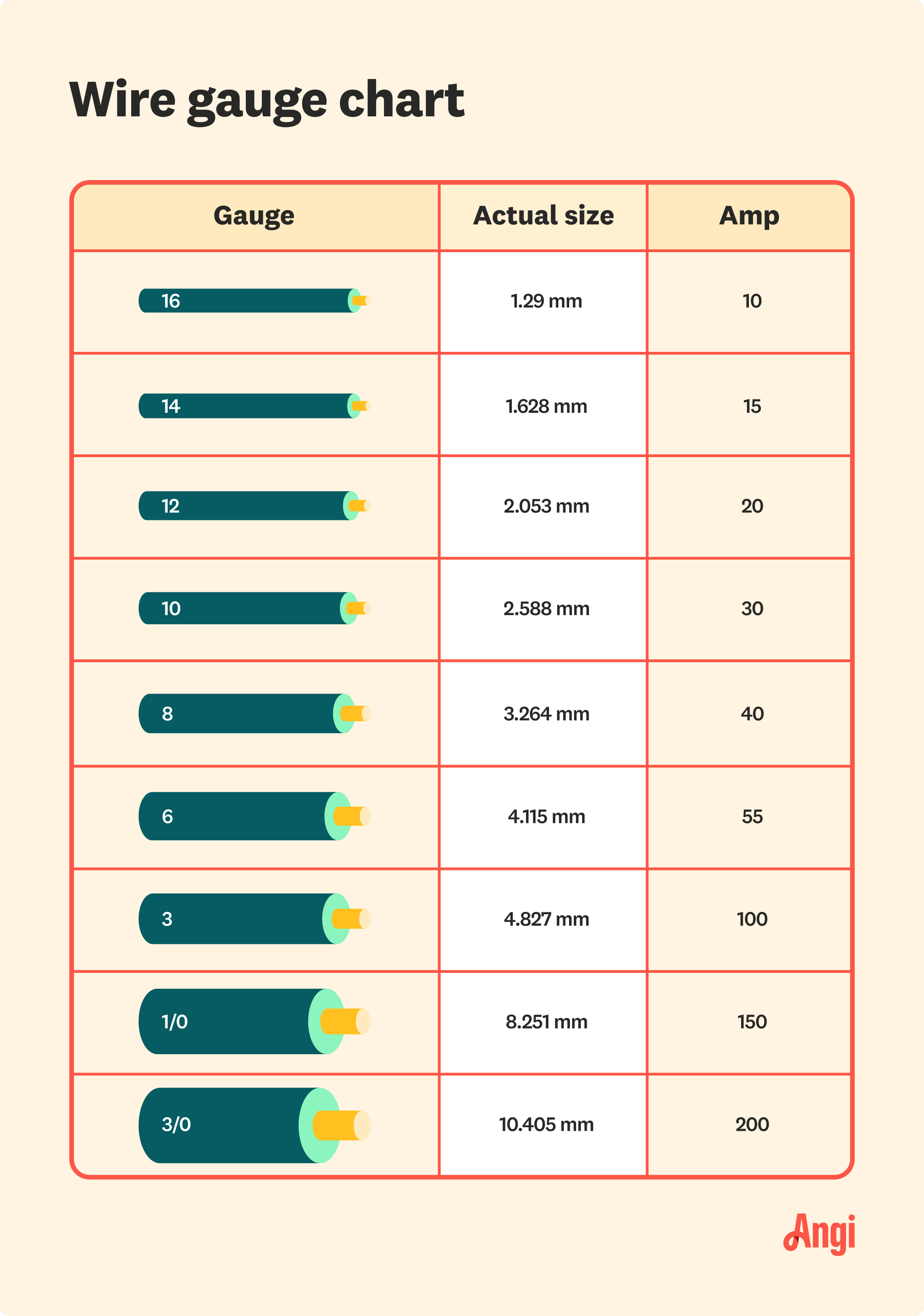
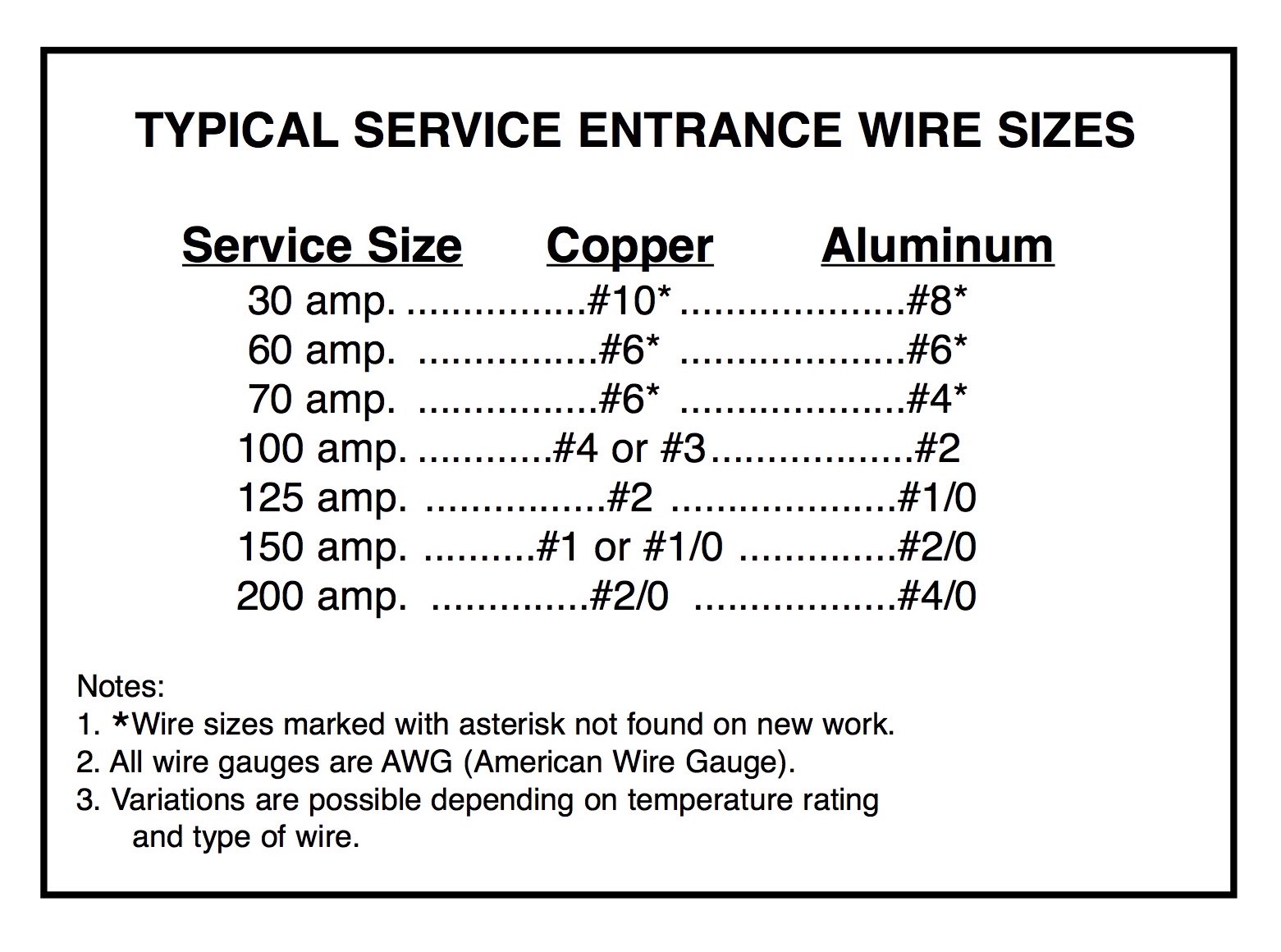
The most common wire size for a 100-amp service is typically 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum. These sizes are recommended for standard installations where the wire runs are relatively short, usually under 100 feet. However, the exact size may vary depending on the specific circumstances of your project. For example, if the wire needs to travel a longer distance, a larger gauge may be required to compensate for voltage drop.
Understanding the relationship between wire size and current capacity is key to making the right choice. A 100-amp service requires a wire that can safely carry 100 amps of current without overheating. Copper wires are more efficient at conducting electricity, which is why they can use a smaller gauge compared to aluminum. If you're unsure about the appropriate size, consulting a licensed electrician or referring to the NEC guidelines is always a good idea.
Why Does Wire Size Matter?
Wire size is critical for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of your electrical system. Using a wire that is too small for the current load can result in excessive heat buildup, which may damage the insulation and pose a fire risk. On the other hand, using a wire that is too large can be unnecessarily expensive and difficult to work with.
What Are the Risks of Choosing the Wrong Size?
- Overheating and potential fire hazards
- Voltage drop leading to inefficient appliance performance
- Non-compliance with electrical codes
- Increased energy costs due to inefficiency
How to Choose the Right Material?
When selecting a wire for a 100-amp service, you'll need to decide between copper and aluminum. Copper is the preferred choice for most residential applications due to its superior conductivity and durability. However, aluminum is a cost-effective alternative that is often used in larger installations, such as subpanels or long-distance runs.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Each Material?
Here’s a quick comparison of copper and aluminum wires:
| Material | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Copper | High conductivity, durable, resistant to corrosion | More expensive, heavier |
| Aluminum | Cost-effective, lightweight | Lower conductivity, requires larger gauge |
What Are the Code Requirements?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides specific guidelines for wire sizing and installation. For a 100-amp service, the NEC requires wires to be rated for the current load and installed in a manner that minimizes voltage drop. Compliance with these codes is not only a legal requirement but also ensures the safety and reliability of your electrical system.
Read also:Barry Weiss The Visionary Leader Transforming Industries
How to Ensure Compliance with the NEC?
To meet NEC requirements, follow these steps:
- Choose the correct wire gauge based on the current load and distance.
- Use wires that are rated for the intended environment (e.g., indoor, outdoor, underground).
- Install wires in accordance with local building codes and manufacturer specifications.
Factors Affecting Wire Size
Several factors influence the size of the wire needed for a 100-amp service. These include the distance between the power source and the load, the material of the wire, and the ambient temperature. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision when selecting the appropriate wire size.
How to Calculate Voltage Drop?
Voltage drop occurs when the electrical resistance of the wire causes a reduction in voltage as the current travels through it. To calculate voltage drop, use the following formula:
Voltage Drop = (2 x Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000
Where:
- Length is the distance of the wire run in feet
- Current is the load in amps
- Resistance is the resistance per 1,000 feet of wire
Can I Use Aluminum Wire?
Yes, aluminum wire can be used for a 100-amp service, but it requires careful consideration. Aluminum wires are larger in diameter than copper wires for the same current capacity, so they may not fit in all connectors or devices. Additionally, aluminum is more prone to corrosion and requires special anti-oxidant compounds during installation.
What Are the Common Mistakes?
Many people make mistakes when selecting and installing wires for a 100-amp service. Some of the most common errors include:
- Underestimating the required wire size
- Ignoring voltage drop calculations
- Using incorrect connectors for aluminum wires
- Failing to comply with local codes and regulations
How to Install 100 Amp Wire?
Installing a 100-amp wire requires careful planning and execution. Here are the steps to follow:
- Turn off the main power supply before starting the installation.
- Measure the distance and calculate the required wire size.
- Choose the appropriate material and gauge based on your calculations.
- Run the wire through conduits or raceways as needed.
- Connect the wire to the breaker panel and the load.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions and answers about what size is 100 amp wire:
What Size is 100 Amp Wire for a Subpanel?
For a subpanel, the wire size is typically the same as for a main panel: 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum. However, the exact size may vary depending on the distance and load requirements.
Can I Use a Smaller Wire for Short Distances?
Yes, for very short distances (under 50 feet), you may be able to use a slightly smaller wire, but it’s always best to stick to the recommended size to ensure safety and compliance.
What Happens If the Wire is Too Small?
If the wire is too small, it can overheat, leading to a fire hazard or damage to your electrical system. Always choose the correct size based on the current load and distance.
Where Can I Find More Information About Wire Sizing?
For more detailed information, consult the National Electrical Code (NEC) or speak with a licensed electrician. They can provide guidance tailored to your specific project needs.