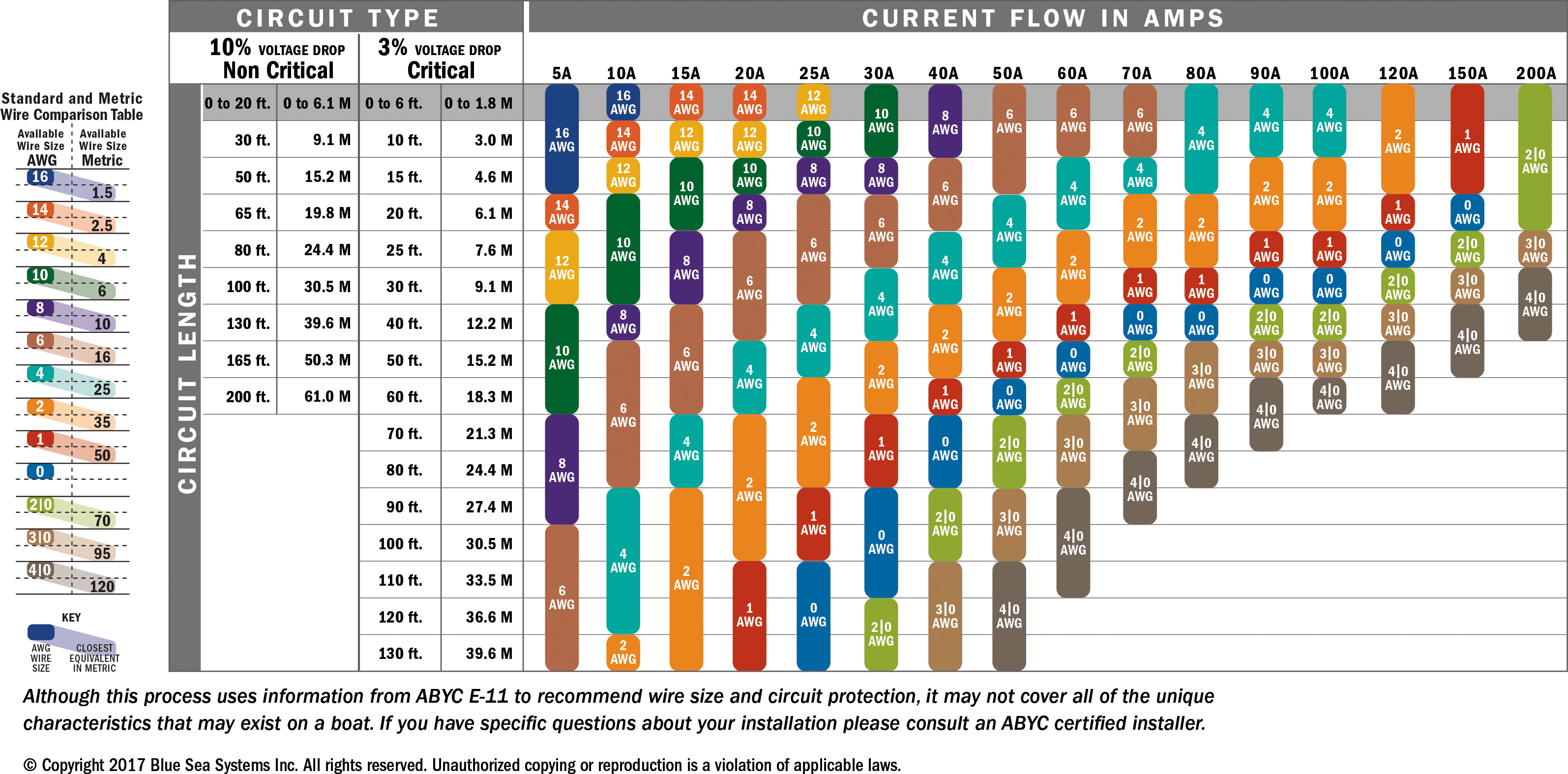
Choosing the right wire size for a 100-amp circuit is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and compliance with electrical codes. Using an undersized wire can lead to overheating, electrical fires, and equipment damage, while an oversized wire may unnecessarily increase costs. Electrical systems rely on properly sized wires to carry current safely, and understanding the factors that determine wire size is essential for homeowners, electricians, and DIY enthusiasts alike. This guide dives deep into the topic of what size wire can handle 100 amps, offering expert advice and practical tips to help you make informed decisions.
When determining the appropriate wire gauge for a 100-amp circuit, several factors come into play, including the type of wire, the length of the run, and the material used (copper or aluminum). Copper wires are more conductive and typically require a smaller gauge than aluminum wires for the same amperage. However, aluminum is often chosen for its cost-effectiveness. Regardless of the material, selecting the correct wire size ensures that your electrical system operates efficiently and avoids potential hazards.
Beyond material and gauge, other considerations like ambient temperature, insulation type, and voltage drop also influence the choice of wire size. For instance, if the wire will be installed in a hot environment, it may need to be upsized to account for reduced conductivity at higher temperatures. Similarly, longer wire runs require thicker gauges to minimize voltage drop and maintain system performance. By addressing these factors, you can confidently answer the question: What size wire can handle 100 amps?
Read also:Szas A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Mastering The Concept
Table of Contents
- What Factors Determine Wire Size for 100 Amps?
- How Do You Calculate Voltage Drop for 100-Amp Circuits?
- Copper vs. Aluminum Wires: Which is Better for 100 Amps?
- What Are the National Electrical Code Requirements for 100-Amp Wire Sizes?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Wire Size
- How to Install a 100-Amp Wire Safely?
- What Are the Best Practices for Maintaining Electrical Wires?
- Tools and Equipment Needed for 100-Amp Wiring Projects
- Frequently Asked Questions About What Size Wire Can Handle 100 Amps
- Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Electrical Needs
What Factors Determine Wire Size for 100 Amps?
Several key factors influence the selection of wire size for a 100-amp circuit. These include the type of wire insulation, the material of the conductor, and the length of the wire run. For instance, wires with higher temperature ratings (such as THHN or THWN) can carry more current than those with lower ratings. Additionally, copper wires are more efficient conductors than aluminum, meaning they can handle the same amperage with a smaller gauge.
Another critical factor is the distance between the power source and the load. Longer runs require thicker wires to compensate for voltage drop, which occurs as electrical current travels through the wire. Voltage drop can reduce the efficiency of your electrical system and cause appliances to underperform. To determine the appropriate wire size, you must calculate the expected voltage drop based on the length of the run and the amperage of the circuit.
Environmental conditions also play a role in wire size selection. If the wire will be exposed to high temperatures, direct sunlight, or moisture, you may need to choose a wire with a higher temperature rating or additional insulation. Understanding these factors ensures that you select the right wire size for your specific application and avoid common pitfalls.
How Do You Calculate Voltage Drop for 100-Amp Circuits?
Calculating voltage drop is essential when determining the appropriate wire size for a 100-amp circuit. Voltage drop occurs because electrical resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage as current flows through it. The formula for calculating voltage drop is:
Voltage Drop = (2 × Length × Current × Resistance) / 1000
Where "Length" is the distance of the wire run in feet, "Current" is the amperage (100 amps in this case), and "Resistance" is the resistance per 1,000 feet of wire, which varies by gauge and material.
Read also:How To Securely Connect Remote Iot Vpc Raspberry Pi Aws Download
For example, a 100-amp circuit with a 100-foot run using 2 AWG copper wire would have a resistance of approximately 0.194 ohms per 1,000 feet. Plugging these numbers into the formula gives:
Voltage Drop = (2 × 100 × 100 × 0.194) / 1000 = 3.88 volts
This represents a voltage drop of 3.88 volts, which is within acceptable limits for most applications. However, if the voltage drop exceeds 3% of the total voltage (e.g., 3.6 volts for a 120-volt system), you may need to increase the wire gauge.
Why Is Voltage Drop Important When Choosing Wire Size?
Voltage drop is critical because it affects the performance of electrical devices and appliances. Excessive voltage drop can cause motors to overheat, lights to dim, and sensitive electronics to malfunction. By understanding how to calculate voltage drop and selecting the appropriate wire size, you can ensure that your electrical system operates efficiently and safely. This is especially important when determining what size wire can handle 100 amps.
Copper vs. Aluminum Wires: Which is Better for 100 Amps?
When it comes to choosing between copper and aluminum wires for a 100-amp circuit, there are pros and cons to consider. Copper is the preferred choice for most applications due to its superior conductivity and durability. It requires a smaller gauge to handle the same amperage as aluminum, making it more space-efficient and easier to work with. However, copper is more expensive, which can be a limiting factor for larger projects.
Aluminum, on the other hand, is lighter and more cost-effective, making it a popular choice for long-distance runs and large-scale installations. However, it has higher resistance than copper, meaning it requires a larger gauge to carry the same current. For example, a 100-amp circuit using aluminum wire typically requires a 1/0 AWG gauge, compared to 2 AWG for copper. Additionally, aluminum is more prone to corrosion and requires special connectors to ensure a secure connection.
Ultimately, the choice between copper and aluminum depends on your budget, the specific requirements of your project, and the environmental conditions. Consulting with a licensed electrician can help you make the best decision for your needs.
What Are the National Electrical Code Requirements for 100-Amp Wire Sizes?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for selecting wire sizes to ensure safety and compliance. According to the NEC, the minimum wire size for a 100-amp service is 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum. These sizes are based on standard conditions, such as a maximum ambient temperature of 30°C (86°F) and a wire run of up to 100 feet.
However, the NEC also allows for adjustments based on specific factors, such as higher ambient temperatures or longer wire runs. For instance, if the wire will be installed in a location with temperatures exceeding 30°C, you may need to increase the wire size to compensate for reduced conductivity. Similarly, if the wire run exceeds 100 feet, you should consider upsizing the wire to minimize voltage drop.
Why Should You Follow NEC Guidelines for 100-Amp Wiring?
Following NEC guidelines ensures that your electrical system is safe, reliable, and compliant with local regulations. Failure to adhere to these standards can result in fines, insurance issues, and even safety hazards. By understanding the NEC requirements for what size wire can handle 100 amps, you can avoid costly mistakes and ensure a successful installation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Wire Size
One of the most common mistakes when selecting wire size for a 100-amp circuit is underestimating the importance of voltage drop. Many people focus solely on the ampacity of the wire, ignoring the impact of long wire runs on performance. This can lead to inefficient systems and potential damage to connected devices.
Another frequent error is using aluminum wire without proper connectors or anti-oxidant compounds. Aluminum is more prone to oxidation, which can cause loose connections and overheating. Always use connectors specifically designed for aluminum wire and apply anti-oxidant paste to ensure a secure and durable connection.
Finally, failing to consult local building codes and regulations can result in non-compliance and safety issues. While the NEC provides a baseline, local codes may have additional requirements that must be followed. Always check with your local authorities before starting any electrical project.
How to Install a 100-Amp Wire Safely?
Installing a 100-amp wire requires careful planning and attention to detail. Start by turning off the power at the main breaker to ensure a safe working environment. Use the appropriate tools, such as wire strippers, crimpers, and conduit benders, to prepare the wire for installation.
Next, route the wire through the conduit or along the designated path, ensuring that it is securely fastened and protected from damage. Avoid sharp bends or kinks in the wire, as these can cause overheating and reduce performance. If using aluminum wire, apply anti-oxidant compound to all connections and use connectors rated for aluminum.
What Safety Precautions Should You Take During Installation?
Safety should always be your top priority when working with electrical systems. Wear insulated gloves and safety glasses to protect yourself from electrical shocks and debris. Use a voltage tester to confirm that the power is off before handling wires. Additionally, ensure that all connections are tight and secure to prevent arcing and overheating.
What Are the Best Practices for Maintaining Electrical Wires?
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and safety of your electrical system. Inspect wires periodically for signs of wear, such as cracks, fraying, or corrosion. Replace damaged wires immediately to prevent hazards.
Keep wires clean and free from dust, debris, and moisture. If wires are exposed to harsh conditions, consider upgrading to more durable insulation or protective conduit. Additionally, test connections periodically to ensure they remain tight and secure.
Tools and Equipment Needed for 100-Amp Wiring Projects
Having the right tools and equipment is crucial for a successful wiring project. Here are some essential items you’ll need:
- Wire strippers
- Crimpers
- Conduit benders
- Voltage tester
- Anti-oxidant compound (for aluminum wires)
Frequently Asked Questions About What Size Wire Can Handle 100 Amps
What Size Wire Can Handle 100 Amps in Copper?
For a 100-amp circuit, the minimum recommended wire size for copper is 2 AWG. This size provides sufficient ampacity and minimizes voltage drop for most standard installations.
What Size Wire Can Handle 100 Amps in Aluminum?
For aluminum wire, the minimum recommended size is 1/0 AWG. Aluminum has higher resistance than copper, so a larger gauge is required to handle the same amperage.
Can I Use a Smaller Wire for a 100-Amp Circuit?
Using a smaller wire than recommended can lead to overheating, voltage drop, and potential fire hazards. Always follow NEC guidelines and consult a professional if you’re unsure.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Electrical Needs
Selecting the correct wire size for a 100-amp circuit is a critical decision that impacts the safety, efficiency, and performance of your electrical system. By considering factors