Whether you're upgrading your home's electrical system, installing a subpanel, or working on an industrial project, knowing the right wire gauge can prevent overheating, electrical fires, and equipment damage. Many homeowners and DIY enthusiasts often wonder, "What size wire do you need for 100 amps?" The answer depends on several factors, including the wire material, the distance of the run, and environmental conditions. In this guide, we'll break down everything you need to know to make an informed decision.
Electrical wiring isn't something to take lightly. Incorrect wire sizing can lead to dangerous situations like overheating, voltage drops, or even complete system failure. For a 100-amp service, the wire must handle the current load without exceeding its capacity. Copper and aluminum are the two most common materials used for wiring, and each has different ampacity ratings. Understanding these differences and how they affect your wiring choice is crucial to ensuring your electrical system operates safely and efficiently.
Beyond material, the length of the wire run plays a significant role in determining the appropriate size. Longer runs require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop, which can affect the performance of your appliances and devices. Additionally, factors like temperature, insulation type, and conduit use can influence the wire size you need. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of what size wire do you need for 100 amps and how to select the best option for your specific application.
Read also:How To Access Iot Devices Anywhere Using Ssh With Aws As An Example
Table of Contents
- Why Wire Size Matters for Electrical Safety
- What Size Wire Do You Need for 100 Amps?
- What Factors Affect the Choice of Wire Size?
- Copper vs. Aluminum: Which is Better for 100-Amp Wiring?
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop for Long Wire Runs?
- What Types of Wire Insulation Are Best for 100-Amp Circuits?
- What Are Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Wire Size?
- What Tools Do You Need for a Safe 100-Amp Wiring Installation?
- Safety Tips for Working with 100-Amp Electrical Systems
- Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Sizing
Why Wire Size Matters for Electrical Safety
When it comes to electrical systems, wire size is not just a technical detail—it's a critical safety factor. The wrong wire size can lead to overheating, which is a leading cause of electrical fires. For a 100-amp service, using a wire that's too small for the current load can result in excessive heat buildup, damaging the insulation and potentially causing a short circuit. On the other hand, using a wire that's unnecessarily large can lead to wasted materials and higher costs.
Electrical codes, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), provide guidelines for wire sizing to ensure safety and efficiency. These codes specify the minimum wire size required for different current loads, taking into account factors like material, insulation, and environmental conditions. By following these guidelines, you can ensure your electrical system is both safe and compliant with local regulations.
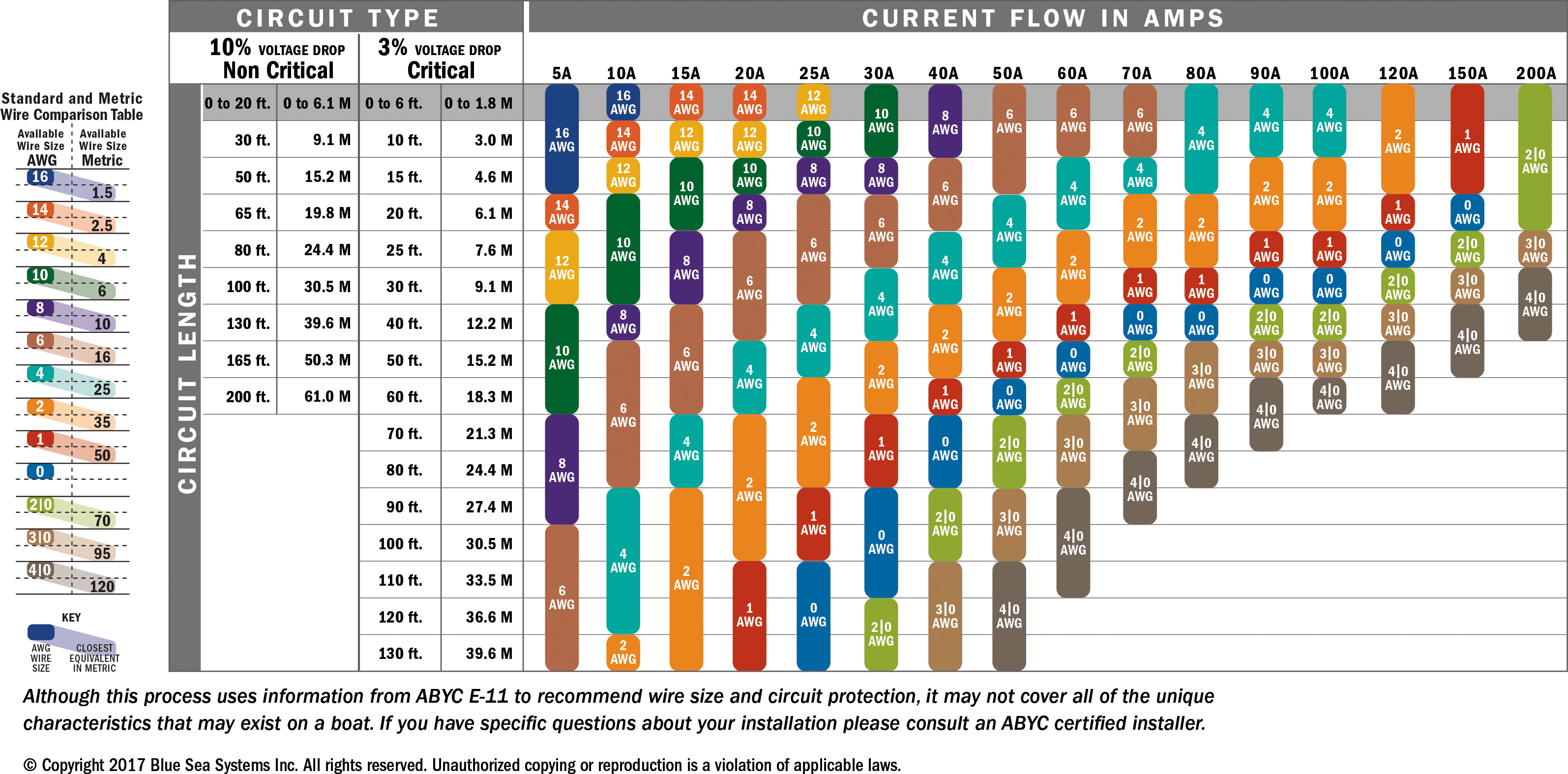
What Size Wire Do You Need for 100 Amps?
For most residential applications, a 100-amp service requires a wire size of 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum. These sizes are based on the NEC's ampacity tables, which specify the maximum current a wire can safely carry. Copper wires are generally preferred for their higher conductivity and smaller size compared to aluminum, but aluminum is often used in larger installations due to its lower cost.
However, these recommendations assume a standard wire run of up to 100 feet. If your installation requires a longer run, you may need to increase the wire size to compensate for voltage drop. Voltage drop occurs when the electrical resistance of the wire causes a reduction in voltage, which can affect the performance of your appliances and devices. To minimize voltage drop, thicker wires are required for longer runs.
What Factors Affect the Choice of Wire Size?
Several factors influence the choice of wire size for a 100-amp service. These include:
- Wire Material: Copper and aluminum have different conductivity levels, affecting the required wire size.
- Wire Length: Longer runs require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop.
- Temperature: High temperatures can reduce a wire's ampacity, necessitating a larger size.
- Insulation Type: Different insulation materials have varying temperature ratings, impacting the wire's capacity.
Copper vs. Aluminum: Which is Better for 100-Amp Wiring?
When deciding between copper and aluminum for a 100-amp service, it's important to weigh the pros and cons of each material. Copper is more conductive and requires a smaller wire size, making it ideal for tight spaces. However, it's also more expensive. Aluminum, on the other hand, is less costly but requires a larger wire size to handle the same current load.
Read also:Exploring Jackie Siegels Net Worth A Deep Dive Into Her Wealth And Lifestyle
For example, a 100-amp service using copper wire typically requires 2 AWG, while aluminum wire needs to be 1/0 AWG. While aluminum is a cost-effective option, it's essential to ensure proper installation techniques to prevent issues like oxidation and loosening connections.
How to Calculate Voltage Drop for Long Wire Runs?
Voltage drop is a critical consideration when determining what size wire do you need for 100 amps. The formula for calculating voltage drop is:
Voltage Drop = (2 x Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000
Where:
- Length is the distance of the wire run in feet.
- Current is the amperage of the circuit (100 amps in this case).
- Resistance is the resistance per 1,000 feet of wire, based on its gauge.
For a 100-amp circuit, a voltage drop of more than 3% is generally considered unacceptable. To minimize voltage drop, you may need to increase the wire size, especially for runs exceeding 100 feet.
What Types of Wire Insulation Are Best for 100-Amp Circuits?
The type of insulation used on the wire also affects its performance and safety. Common insulation types include THHN, XHHW, and UF-B. THHN is suitable for dry and damp locations, while XHHW is designed for wet environments. UF-B is ideal for underground installations.
Choosing the right insulation ensures the wire can withstand environmental conditions and operate safely under load. For a 100-amp service, THHN or XHHW insulation is typically recommended due to their high-temperature ratings and durability.
What Are Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Wire Size?
Even experienced electricians can make mistakes when selecting wire size for a 100-amp service. Some common errors include:
- Underestimating the wire size needed for long runs.
- Ignoring environmental factors like temperature and moisture.
- Using aluminum wire without proper connectors or anti-oxidation paste.
- Overlooking local electrical codes and regulations.
Avoiding these mistakes ensures your electrical system is safe, efficient, and compliant with standards.
What Tools Do You Need for a Safe 100-Amp Wiring Installation?
Installing a 100-amp service requires the right tools to ensure safety and accuracy. Essential tools include:
- Wire strippers and cutters.
- Voltage testers.
- Torque wrenches for tightening connections.
- Conduit benders for routing wires.
Using the correct tools not only makes the job easier but also reduces the risk of errors and accidents.
Safety Tips for Working with 100-Amp Electrical Systems
Working with a 100-amp electrical system can be dangerous if proper precautions aren't taken. Always:
- Turn off the power before starting any work.
- Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shocks.
- Follow all local electrical codes and regulations.
- Hire a licensed electrician if you're unsure about any aspect of the installation.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Sizing
Q: What size wire do you need for 100 amps in a residential setting?
A: For most residential applications, a 2 AWG copper wire or 1/0 AWG aluminum wire is recommended for a 100-amp service.
Q: How does wire length affect the size needed for 100 amps?
A: Longer wire runs require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop and ensure efficient performance.
Q: Can I use aluminum wire for a 100-amp service?
A: Yes, but aluminum wire requires a larger gauge (1/0 AWG) compared to copper (2 AWG) and must be installed with proper connectors and anti-oxidation measures.
Q: What insulation type is best for a 100-amp circuit?
A: THHN or XHHW insulation is typically recommended for 100-amp circuits due to their high-temperature ratings and durability.
Q: How do I calculate voltage drop for a 100-amp circuit?
A: Use the formula: Voltage Drop = (2 x Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000, and ensure the drop is within acceptable limits (less than 3%).