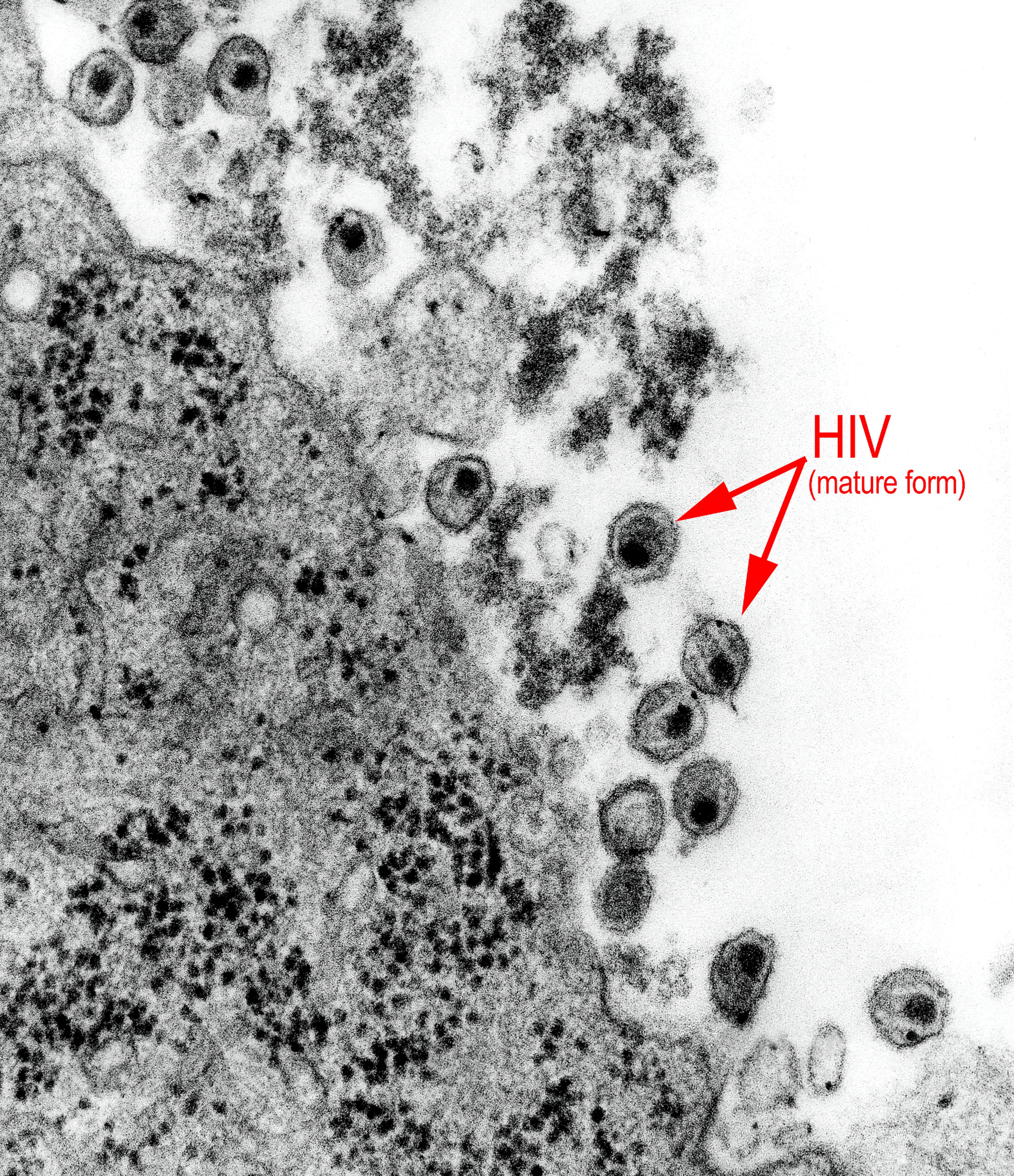
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) remains one of the most significant global health challenges today, affecting millions of lives worldwide. This virus targets the immune system, specifically the CD4 cells, weakening the body's ability to fight infections and diseases. Without proper treatment, HIV can progress to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), a life-threatening condition. Understanding HIV, its causes, symptoms, and prevention methods is crucial for reducing its spread and improving the quality of life for those affected. This article dives deep into the topic, offering valuable insights to help you stay informed and take proactive steps.
Despite advancements in medical science, misconceptions about HIV persist, leading to stigma and discrimination. Educating yourself about the virus is the first step toward breaking down these barriers. From its origins to its impact on individuals and communities, HIV is a complex topic that requires clarity and accuracy. By exploring its transmission, symptoms, and available treatments, we aim to provide a comprehensive guide that addresses common concerns and empowers readers with knowledge.
Living with HIV is no longer a death sentence, thanks to groundbreaking research and antiretroviral therapies. These treatments allow individuals to lead long, healthy lives while managing the virus effectively. However, early detection and consistent care remain vital. This article is designed to equip you with the tools to recognize the signs of HIV, understand its effects on the body, and learn how to protect yourself and others from infection. Let’s explore the critical aspects of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and how we can work together to combat this global issue.
Read also:Who Is Apolo Ohnos Wife A Complete Guide To The Olympic Champions Life And Love
Table of Contents
- What is Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)?
- How Does HIV Spread?
- What Are the Symptoms of HIV?
- Can HIV Be Cured?
- How to Prevent Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
- What Are the Stages of HIV Infection?
- How is HIV Diagnosed?
- What Are the Treatment Options for HIV?
- How Does HIV Affect Daily Life?
- What Are the Future Prospects for HIV Research?
What is Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks the immune system, specifically targeting CD4 cells, which are crucial for fighting infections. Over time, HIV reduces the number of these cells, making the body more vulnerable to opportunistic infections and certain cancers. If left untreated, HIV can progress to AIDS, the most severe stage of the infection. AIDS is defined by a CD4 count below 200 cells per cubic millimeter or the development of specific illnesses.
HIV is classified into two types: HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV-1 is the most common and widespread type, while HIV-2 is primarily found in West Africa. Both types damage the immune system, but HIV-2 progresses more slowly and is less transmissible. Understanding the differences between these types is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
How Does HIV Spread?
HIV is transmitted through specific bodily fluids, including blood, semen, vaginal fluids, rectal fluids, and breast milk. The most common modes of transmission include unprotected sexual intercourse, sharing needles or syringes, and mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding. It is important to note that HIV cannot spread through casual contact such as hugging, kissing, or sharing food.
What Are the Risk Factors for HIV Transmission?
Several factors increase the risk of contracting human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These include engaging in unprotected sex, having multiple sexual partners, and using contaminated needles. Individuals with other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are also at a higher risk of acquiring HIV due to the increased likelihood of transmission.
Can HIV Be Transmitted Through Blood Transfusions?
In most developed countries, the risk of HIV transmission through blood transfusions is extremely low due to rigorous screening processes. However, in regions with limited resources, this remains a concern. Always ensure that blood products are sourced from reputable facilities to minimize risks.
What Are the Symptoms of HIV?
The symptoms of HIV vary depending on the stage of infection. During the acute phase, which occurs 2-4 weeks after exposure, individuals may experience flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, rash, night sweats, muscle aches, sore throat, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, and mouth ulcers. These symptoms often go unnoticed or are mistaken for other illnesses.
Read also:How To Securely Connect Remote Iot Vpc Raspberry Pi Aws Download
What Happens During the Chronic Phase of HIV?
After the acute phase, HIV enters a latent or chronic stage where the virus continues to multiply at low levels. During this period, individuals may not experience any symptoms, but the virus is still active and can be transmitted to others. Regular testing is essential to detect HIV early and begin treatment.
Can HIV Be Cured?
Currently, there is no cure for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). However, antiretroviral therapy (ART) has revolutionized HIV management, allowing individuals to live long and healthy lives. ART works by suppressing the virus to undetectable levels, reducing the risk of transmission and preventing the progression to AIDS.
Is an Undetectable Viral Load the Same as a Cure?
An undetectable viral load means that the amount of HIV in the blood is so low that it cannot be detected by standard tests. While this does not eliminate the virus from the body, it significantly improves health outcomes and reduces the risk of transmission. This concept is often referred to as "U=U" (Undetectable = Untransmittable).
How to Prevent Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
Preventing HIV involves a combination of strategies, including practicing safe sex, using condoms consistently, and avoiding shared needles. Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) are additional preventive measures that can reduce the risk of infection.
What Role Does Education Play in HIV Prevention?
Educating individuals about human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and its transmission is critical for prevention. Awareness campaigns, school programs, and community initiatives can help dispel myths and encourage responsible behavior, ultimately reducing the spread of the virus.
Can Vaccines Prevent HIV?
Currently, there is no vaccine available to prevent HIV. However, researchers are actively working on developing one. In the meantime, focusing on proven prevention methods remains the best approach to reducing new infections.
What Are the Stages of HIV Infection?
HIV infection progresses through three main stages: acute HIV infection, chronic HIV infection, and AIDS. Each stage has distinct characteristics and requires specific medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can slow the progression of the virus and improve long-term outcomes.
How Long Does It Take for HIV to Progress to AIDS?
Without treatment, HIV typically progresses to AIDS within 10-15 years. However, with antiretroviral therapy, individuals can maintain their health and delay the onset of AIDS indefinitely.
How is HIV Diagnosed?
HIV is diagnosed through various tests, including antibody tests, antigen/antibody tests, and nucleic acid tests (NATs). These tests detect the presence of HIV antibodies, antigens, or the virus itself in the blood. Early testing is crucial for timely intervention and treatment.
Why Is Regular Testing Important?
Regular testing for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) ensures early detection and access to treatment. It also helps prevent the spread of the virus by identifying individuals who may unknowingly transmit it to others.
What Are the Treatment Options for HIV?
Treatment for HIV primarily involves antiretroviral therapy (ART), which combines multiple medications to suppress the virus. Adherence to ART is essential for maintaining an undetectable viral load and improving overall health. Supportive therapies may also be prescribed to manage symptoms and complications.
What Are the Side Effects of ART?
While ART is highly effective, it can cause side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, and headaches. These symptoms often improve over time, and healthcare providers can adjust medications to minimize discomfort.
How Does HIV Affect Daily Life?
Living with HIV requires ongoing medical care, adherence to treatment, and lifestyle adjustments. However, with proper management, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Support groups and counseling services can provide emotional and psychological support.
What Challenges Do People with HIV Face?
Stigma and discrimination remain significant challenges for individuals living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Advocacy and education efforts are essential to create a more inclusive and supportive environment.
What Are the Future Prospects for HIV Research?
Researchers are making significant strides in HIV research, exploring new treatments, vaccines, and potential cures. Advances in gene editing and immunotherapy offer promising possibilities for the future of HIV management.
How Can We Accelerate Progress in HIV Research?
Increased funding, collaboration, and public awareness are key to accelerating progress in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) research. Supporting organizations and initiatives dedicated to HIV eradication can make a meaningful impact.