Wire gauge size refers to the diameter of a wire, which directly impacts its current-carrying capacity and resistance. Using the wrong gauge can lead to overheating, electrical failures, or even fire hazards. With so many options available, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. However, by learning how to identify and measure wire gauge size, you can ensure your projects are safe and efficient. This article will cover tools, techniques, and tips to help you confidently determine the correct wire gauge size for any application.
Whether you're wiring a new home, repairing an appliance, or working on a hobby project, knowing the wire gauge size is crucial. In this guide, we'll answer common questions like "What tools do I need to measure wire gauge size?" and "How does wire gauge affect electrical performance?" By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of how to know wire gauge size and the confidence to apply this knowledge in real-world scenarios.
Table of Contents
- What is Wire Gauge?
- Why Does Wire Gauge Matter?
- How to Measure Wire Gauge Size?
- What Tools Do You Need to Measure Wire Gauge?
- What Are the Most Common Wire Gauge Sizes?
- How Does Wire Gauge Affect Electrical Performance?
- How to Choose the Right Wire Gauge for Your Project?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Determining Wire Gauge Size
- Tips for DIY Projects: How to Know Wire Gauge Size
- Final Thoughts on Wire Gauge Size
What is Wire Gauge?
Wire gauge is a standardized measurement system used to describe the diameter of a wire. The most common system in use today is the American Wire Gauge (AWG), which assigns a numerical value to each gauge size. The higher the gauge number, the thinner the wire. For example, a 14-gauge wire is thinner than a 10-gauge wire. Understanding this system is the first step in learning how to know wire gauge size.
Read also:Barry Weiss The Visionary Leader Transforming Industries
Why Does Wire Gauge Matter?
Wire gauge directly affects the amount of current a wire can safely carry. Using a wire that's too thin for the current it needs to handle can lead to overheating and potential hazards. On the other hand, using a wire that's too thick can be unnecessarily expensive and cumbersome. Knowing how to determine wire gauge size ensures that your electrical systems are both safe and cost-effective.
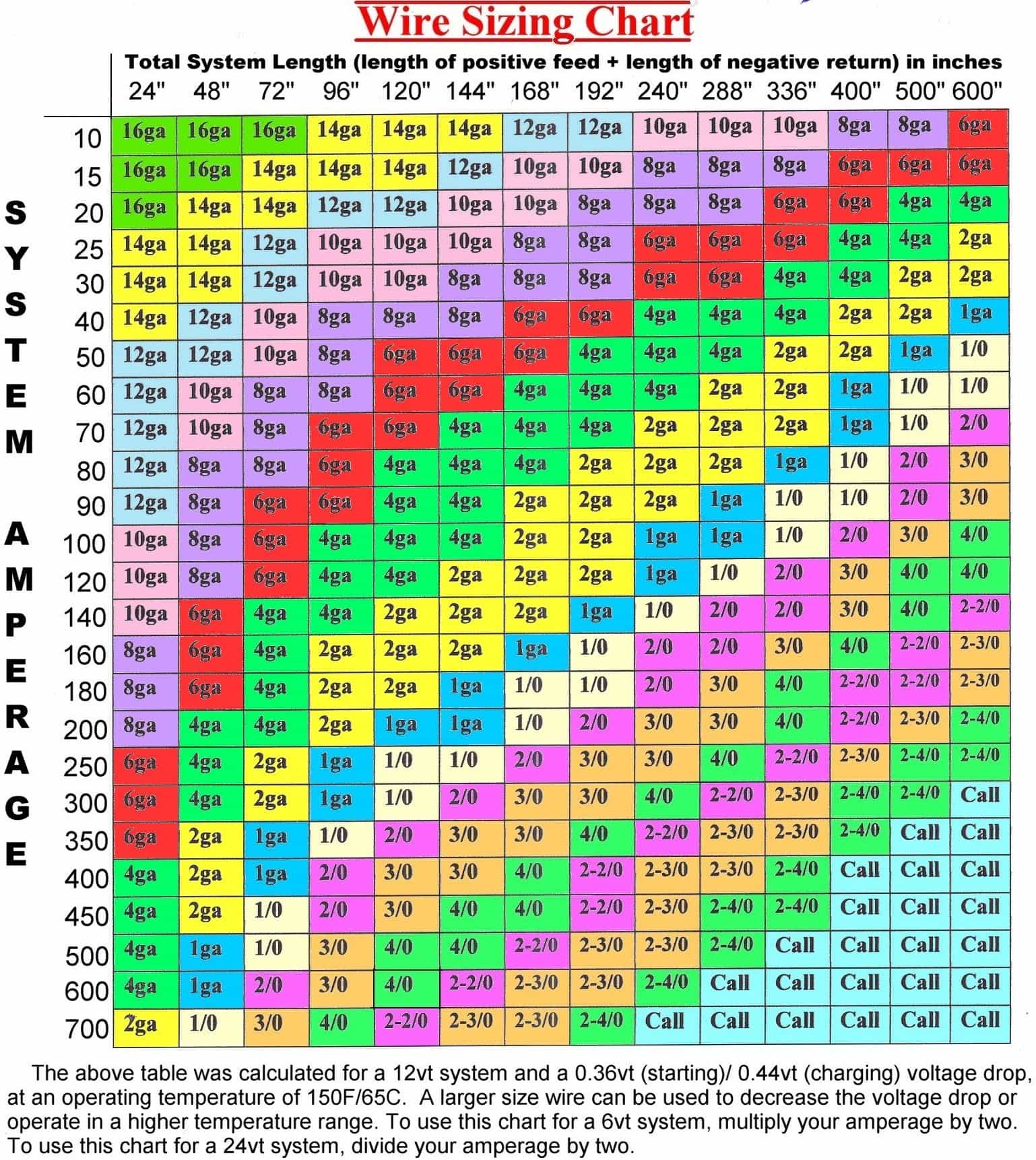
How to Measure Wire Gauge Size?
Measuring wire gauge size can be done using a few simple tools. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Obtain a wire gauge measuring tool, such as a wire stripper or caliper.
- Strip the insulation from the wire to expose the metal conductor.
- Insert the wire into the appropriate slot on the measuring tool or use the caliper to measure its diameter.
- Compare the measurement to a wire gauge chart to determine the gauge size.
What Tools Do You Need to Measure Wire Gauge?
Having the right tools is crucial for accurately determining wire gauge size. Here are some commonly used tools:
- Wire Gauge Tool: A specialized tool with slots for different gauge sizes.
- Calipers: Precision instruments for measuring the diameter of the wire.
- Wire Strippers: Tools that can strip insulation and often include gauge markings.
What Are the Most Common Wire Gauge Sizes?
Some wire gauge sizes are more commonly used than others, depending on the application. Here are a few examples:
- 14-Gauge: Commonly used for lighting circuits.
- 12-Gauge: Ideal for outlets and small appliances.
- 10-Gauge: Suitable for larger appliances like air conditioners.
- 8-Gauge: Used for heavy-duty applications like electric ranges.
How Does Wire Gauge Affect Electrical Performance?
The gauge of a wire influences its resistance and current-carrying capacity. Thicker wires (lower gauge numbers) have less resistance and can carry more current without overheating. Thinner wires (higher gauge numbers) have higher resistance, which can lead to voltage drops and inefficiencies. Understanding how to know wire gauge size is essential for optimizing electrical performance.
How to Choose the Right Wire Gauge for Your Project?
Selecting the correct wire gauge involves considering several factors:
Read also:Edward Ruttle A Comprehensive Guide To His Life Legacy And Achievements
- Current Load: Determine the maximum current the wire will need to carry.
- Distance: Longer runs require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop.
- Application: Different applications have specific gauge requirements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Determining Wire Gauge Size
Here are some common pitfalls to watch out for:
- Using a wire that's too thin for the current load.
- Ignoring the length of the wire run.
- Failing to consult a wire gauge chart.
Tips for DIY Projects: How to Know Wire Gauge Size
If you're working on a DIY project, here are some tips to help you determine wire gauge size:
- Always consult a wire gauge chart before starting your project.
- Invest in a good-quality wire gauge tool or caliper.
- Double-check your measurements to ensure accuracy.
Final Thoughts on Wire Gauge Size
Knowing how to determine wire gauge size is a valuable skill for anyone working with electrical systems. By understanding the basics of wire gauge, using the right tools, and avoiding common mistakes, you can ensure your projects are safe, efficient, and up to code. Remember, when in doubt, consult a professional electrician to ensure your wiring meets all necessary standards. With this guide, you're well-equipped to tackle any project that requires knowledge of how to know wire gauge size.