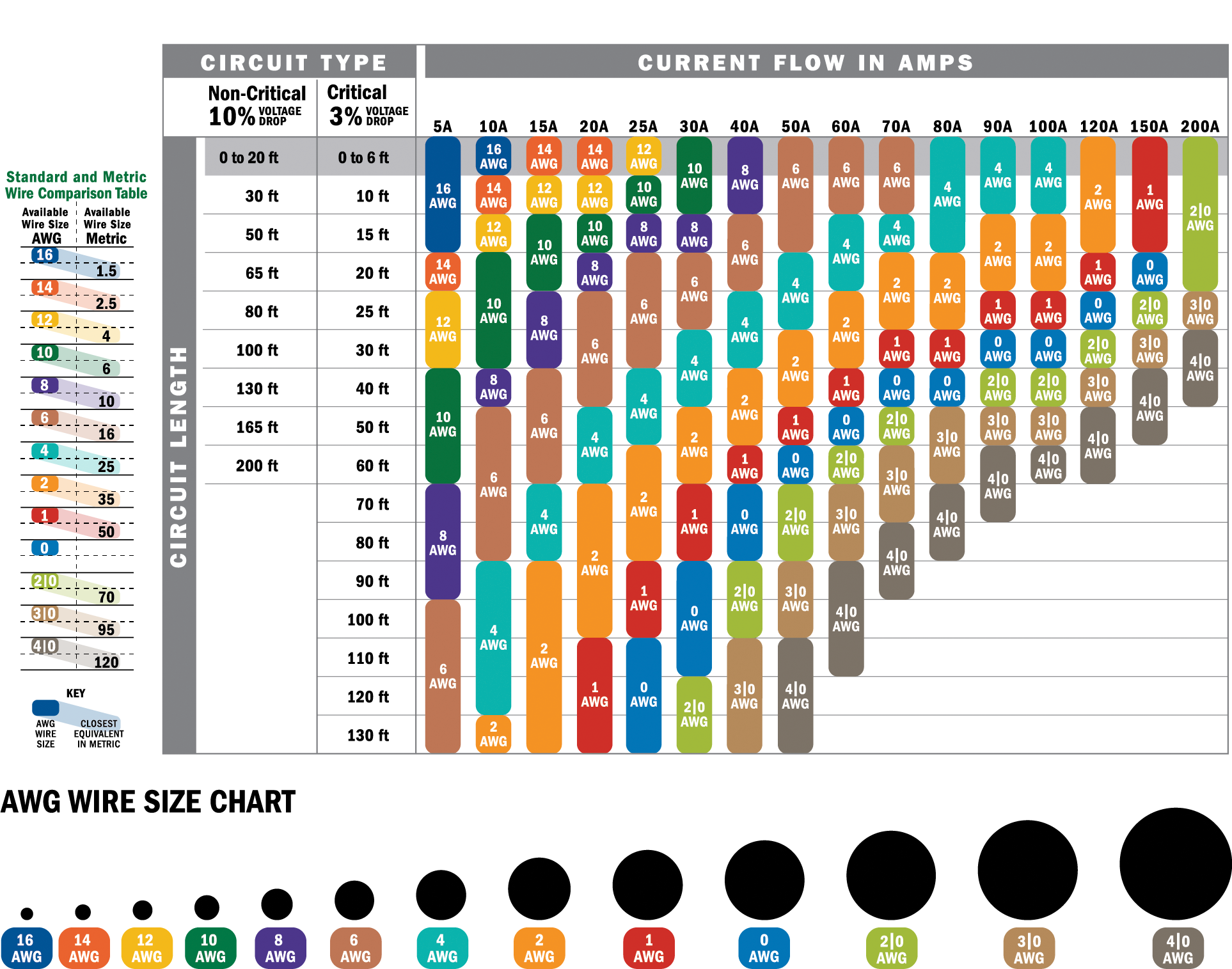
When it comes to electrical wiring, choosing the right gauge wire is crucial for safety and efficiency. The 8 gauge wire amps capacity is a popular choice for various applications, from residential wiring to automotive projects. Understanding its ampacity, limitations, and uses can help you make informed decisions for your electrical needs. Whether you're an electrician, a DIY enthusiast, or someone looking to expand their knowledge, this guide will provide all the essential details about 8 gauge wire amps.
Electrical safety is not something to be taken lightly, and knowing the ampacity of your wire is a key step in ensuring a safe installation. An 8 gauge wire is designed to handle a specific amount of current, typically rated for 40-55 amps depending on factors like insulation type and ambient temperature. This makes it suitable for high-power appliances, circuits, and equipment. With its versatility, 8 gauge wire amps are commonly used in scenarios where medium to heavy electrical loads are expected.
Many people wonder how to determine if 8 gauge wire is the right choice for their project. Factors like the length of the wire, the type of load, and environmental conditions all play a role in this decision. This article will explore the technical specifications of 8 gauge wire amps, address common questions, and provide practical advice to ensure you use it effectively and safely. Let's dive deeper into the details to help you understand everything you need to know.
Read also:Jaden Smith P Diddy Unveiling Their Influence Legacy And Impact
Table of Contents
- What is 8 Gauge Wire Amps?
- How Many Amps Can 8 Gauge Wire Handle?
- Is 8 Gauge Wire Safe for High-Power Applications?
- Common Uses of 8 Gauge Wire Amps
- Factors Affecting 8 Gauge Wire Performance
- How to Choose the Right Wire for Your Project?
- What Are the Risks of Using the Wrong Wire Gauge?
- How Does Temperature Affect 8 Gauge Wire Amps?
- Practical Tips for Working with 8 Gauge Wire
- Conclusion and Final Thoughts
What is 8 Gauge Wire Amps?
8 gauge wire amps refer to the amount of electrical current that an 8-gauge wire can safely carry without overheating or causing damage. This measurement is known as ampacity and is determined by factors such as the wire's material (copper or aluminum), insulation type, and environmental conditions. For most applications, an 8 gauge wire is rated to handle between 40 and 55 amps, making it suitable for medium to heavy electrical loads.
The ampacity of a wire is critical because exceeding its capacity can lead to overheating, which poses a significant fire hazard. This is why understanding the 8 gauge wire amps capacity is essential for anyone working on electrical projects. Whether you're wiring a new circuit in your home or installing a car audio system, knowing the limits of your wire ensures safety and reliability.
Additionally, the 8 gauge wire is often used in scenarios where longer wire runs are required. This is because it has a lower resistance compared to thinner wires, reducing voltage drop over distance. By minimizing voltage drop, you can ensure that your devices receive the correct amount of power, improving their performance and lifespan.
How Many Amps Can 8 Gauge Wire Handle?
One of the most frequently asked questions about 8 gauge wire is its ampacity. The answer depends on several factors, including the type of insulation and the ambient temperature. For example, a copper 8 gauge wire with THHN insulation can typically handle up to 55 amps, while aluminum wire of the same gauge might be rated for slightly less.
It's important to note that these ratings are based on ideal conditions. If the wire is exposed to high temperatures or bundled with other wires, its ampacity may decrease. This is why electricians often derate the wire's capacity to ensure safety. For instance, in a hot environment, an 8 gauge wire amps capacity might be reduced to 40 amps to prevent overheating.
Read also:Barry Weiss The Visionary Leader Transforming Industries
When planning your project, always refer to the National Electrical Code (NEC) or consult a professional to determine the appropriate ampacity for your specific situation. This ensures compliance with safety standards and reduces the risk of electrical hazards.
Is 8 Gauge Wire Safe for High-Power Applications?
Yes, 8 gauge wire is generally safe for high-power applications, provided it is used within its rated capacity. Its ability to handle up to 55 amps makes it suitable for devices like air conditioners, electric heaters, and large appliances. However, safety depends on proper installation and adherence to guidelines.
For example, if you're using 8 gauge wire amps for a circuit in your home, ensure that the breaker matches the wire's capacity. Using a breaker with a higher rating than the wire can handle is a recipe for disaster, as it may allow too much current to flow, leading to overheating and potential fire hazards.
Another consideration is the wire's insulation. Different types of insulation have varying temperature ratings, which affect the wire's ampacity. For instance, wires with THHN insulation can handle higher temperatures than those with PVC insulation. Always choose the appropriate insulation type for your application to maximize safety and performance.
Common Uses of 8 Gauge Wire Amps
The versatility of 8 gauge wire amps makes it a popular choice for a wide range of applications. Below are some common uses:
- Residential Wiring: Ideal for circuits powering large appliances like ovens, dryers, and HVAC systems.
- Automotive Projects: Used in car audio systems, amplifiers, and battery connections.
- Outdoor Installations: Suitable for wiring outdoor lighting, hot tubs, and pool equipment.
- Industrial Applications: Commonly used in machinery and equipment that require high current loads.
Each of these applications benefits from the 8 gauge wire's ability to handle significant electrical loads without overheating. Its durability and reliability make it a go-to choice for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
Factors Affecting 8 Gauge Wire Performance
Several factors can influence the performance of 8 gauge wire amps. Understanding these factors is essential for ensuring optimal functionality and safety:
- Wire Material: Copper wires have higher conductivity than aluminum, making them more efficient for carrying current.
- Insulation Type: Different insulation materials have varying temperature and environmental resistance.
- Ambient Temperature: Higher temperatures can reduce the wire's ampacity, requiring derating.
- Wire Length: Longer wires experience more voltage drop, which can affect device performance.
By considering these factors, you can make informed decisions about using 8 gauge wire amps in your projects.
How to Choose the Right Wire for Your Project?
Choosing the right wire involves evaluating your project's specific needs. Here are some tips to help you select the appropriate wire:
- Calculate the total current load of your devices to determine the required ampacity.
- Consider the distance between the power source and the device to minimize voltage drop.
- Check local electrical codes and regulations to ensure compliance.
- Consult with a licensed electrician if you're unsure about the best wire for your application.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your project is both safe and efficient.
What Are the Risks of Using the Wrong Wire Gauge?
Using the wrong wire gauge can lead to serious consequences, including overheating, electrical fires, and equipment damage. For example, using a wire with a lower gauge than required for 8 gauge wire amps can result in excessive heat buildup, which may melt the insulation and cause short circuits.
On the other hand, using a wire with a higher gauge than necessary can be wasteful and unnecessarily expensive. It's essential to match the wire gauge to the current load to ensure safety and efficiency.
How Does Temperature Affect 8 Gauge Wire Amps?
Temperature plays a significant role in determining the ampacity of 8 gauge wire. Higher temperatures can reduce the wire's ability to dissipate heat, leading to a lower ampacity rating. This is why electricians often derate wires in hot environments to prevent overheating.
For example, if you're installing 8 gauge wire amps in an attic or garage where temperatures can rise significantly, you may need to reduce its ampacity to ensure safe operation. Always consider the environment when planning your electrical projects.
Practical Tips for Working with 8 Gauge Wire
Working with 8 gauge wire requires care and attention to detail. Here are some practical tips to help you get the most out of your project:
- Use proper tools, such as wire strippers and crimpers, to ensure clean connections.
- Avoid overloading the wire by calculating the total current load beforehand.
- Secure the wire properly to prevent damage from movement or abrasion.
- Label your wires clearly to make future maintenance easier.
By following these tips, you can ensure a successful and safe installation.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Understanding 8 gauge wire amps is essential for anyone working on electrical projects. Its ability to handle high current loads makes it a versatile and reliable choice for a wide range of applications. By considering factors like ampacity, insulation, and environmental conditions, you can ensure that your projects are both safe and efficient.
Whether you're wiring a new circuit in your home or installing a car audio system, the 8 gauge wire amps capacity provides the performance and reliability you need. Always follow safety guidelines, consult professionals when necessary, and prioritize quality materials to achieve the best results.