When it comes to electrical wiring, safety and efficiency are paramount, and choosing the correct wire gauge is crucial for optimal performance. A 40 amp wire gauge is often required for circuits that demand higher power, such as large appliances, air conditioners, or electric vehicle chargers. Understanding the specifications and applications of this wire gauge ensures that your electrical system operates safely and efficiently. Incorrect wire sizing can lead to overheating, voltage drops, and even fire hazards, making it essential to get it right.
Many homeowners and DIY enthusiasts find themselves puzzled when selecting the appropriate wire for their 40-amp circuits. The right wire gauge not only ensures the smooth flow of electricity but also complies with local electrical codes. Factors such as the length of the wire, the material (copper or aluminum), and the environment in which the wire will be installed play a significant role in determining the correct gauge. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about the 40 amp wire gauge, helping you make informed decisions.
Whether you're an electrician, a DIY enthusiast, or simply someone looking to upgrade your home's electrical system, this article will provide you with valuable insights. From understanding the basics of wire gauges to answering frequently asked questions, we’ve got you covered. Keep reading to explore the intricacies of the 40 amp wire gauge and how it can be applied in various scenarios to ensure safety and performance.
Read also:Best Free Web Ssh Access For Iot Devices On Raspberry Pi
Table of Contents
- What is a 40 Amp Wire Gauge?
- Why is the Right Wire Gauge Important?
- How Do You Choose the Right Wire for a 40 Amp Circuit?
- Can You Use a Smaller Gauge for a 40 Amp Circuit?
- What Materials Are Best for a 40 Amp Wire?
- What Are the Common Applications of a 40 Amp Wire Gauge?
- How Does Wire Length Affect the 40 Amp Wire Gauge Choice?
- What Are the Safety Tips for Using a 40 Amp Wire?
- How Can You Avoid Common Mistakes with a 40 Amp Wire Gauge?
- Frequently Asked Questions About 40 Amp Wire Gauges
What is a 40 Amp Wire Gauge?
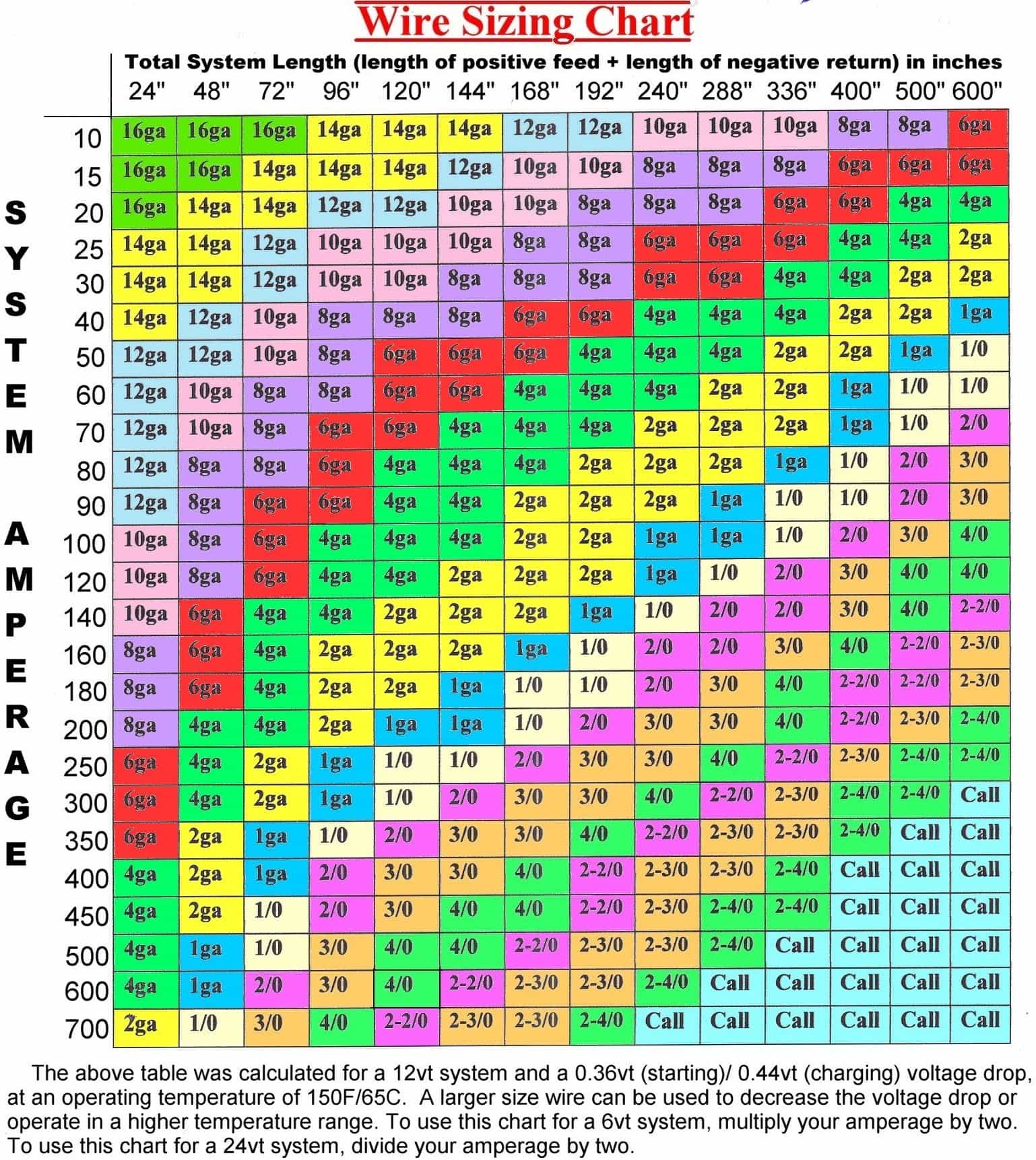
A 40 amp wire gauge refers to the size of the wire that can safely carry 40 amps of electrical current. Wire gauges are standardized measurements that indicate the diameter of the wire, with lower numbers representing thicker wires. For a 40-amp circuit, the most commonly recommended wire gauge is 8 AWG (American Wire Gauge) for copper wires. However, if aluminum wire is used, a thicker gauge, such as 6 AWG, is typically required due to its lower conductivity compared to copper.
The choice of wire gauge is influenced by the amount of current the wire needs to carry and the distance it must travel. Using an undersized wire can lead to overheating, while an oversized wire may be unnecessarily expensive. Understanding the 40 amp wire gauge ensures that your electrical system operates within safe parameters.
Why is the Right Wire Gauge Important?
Choosing the correct wire gauge is critical for preventing electrical hazards. When a wire is too small for the current it carries, it can overheat, melt its insulation, and potentially cause a fire. On the other hand, using a wire that is too large for the circuit can be costly and impractical. The 40 amp wire gauge is specifically designed to handle the current load of 40 amps, ensuring safe and efficient energy transfer.
Additionally, using the correct wire gauge ensures compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local regulations. These codes are in place to protect both property and lives, making it essential to adhere to them when installing or upgrading electrical systems.
How Do You Choose the Right Wire for a 40 Amp Circuit?
Choosing the right wire for a 40-amp circuit involves considering several factors. First, determine whether you’ll be using copper or aluminum wire. Copper is more conductive and can carry more current than aluminum, making it a popular choice for residential wiring. For a 40-amp circuit, 8 AWG copper wire is typically recommended, while 6 AWG aluminum wire is often used.
Next, consider the length of the wire run. Longer distances require thicker wires to compensate for voltage drop. A voltage drop occurs when the resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage, which can affect the performance of connected devices. For most residential applications, a voltage drop of no more than 3% is acceptable.
Read also:Chris Bledsoe Net Worth A Comprehensive Overview Of His Financial Success
Finally, think about the environment where the wire will be installed. If the wire will be exposed to moisture, extreme temperatures, or corrosive substances, you may need to choose a wire with specialized insulation, such as THHN or UF cable.
Can You Use a Smaller Gauge for a 40 Amp Circuit?
Using a smaller gauge wire for a 40-amp circuit is strongly discouraged. Smaller wires have higher resistance, which can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. For example, a 10 AWG wire is rated for 30 amps, not 40 amps, and using it for a 40-amp circuit would exceed its safe capacity.
Always consult the NEC guidelines or a licensed electrician to ensure that the wire gauge you choose is appropriate for your specific application. Cutting corners by using a smaller gauge wire can compromise safety and lead to costly repairs or replacements in the future.
What Materials Are Best for a 40 Amp Wire?
When selecting materials for a 40 amp wire, copper and aluminum are the two most common options. Copper is preferred for its superior conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion. It is also easier to work with, making it a popular choice for residential wiring.
Aluminum, while less expensive, is less conductive and requires a larger gauge to carry the same amount of current as copper. It is also more prone to corrosion and requires special connectors to prevent oxidation. Despite these drawbacks, aluminum is still widely used in commercial and industrial settings due to its cost-effectiveness.
Regardless of the material you choose, ensure that the wire is rated for the specific application and environment in which it will be installed. This ensures both safety and longevity of the electrical system.
What Are the Common Applications of a 40 Amp Wire Gauge?
The 40 amp wire gauge is commonly used in applications that require higher power, such as:
- Electric vehicle (EV) charging stations
- Central air conditioning units
- Electric water heaters
- Large kitchen appliances, such as ranges and ovens
- Workshops with heavy-duty tools and equipment
These applications demand a wire gauge that can handle the high current without overheating or causing voltage drops. The 40 amp wire gauge is specifically designed to meet these requirements, making it an essential component of many electrical systems.
How Does Wire Length Affect the 40 Amp Wire Gauge Choice?
Wire length plays a significant role in determining the appropriate 40 amp wire gauge. Longer wire runs experience higher resistance, which can lead to voltage drop. To compensate for this, thicker wires are often required to maintain safe and efficient energy transfer.
For example, if you’re running a 40-amp circuit over a distance of 100 feet, you may need to upgrade from 8 AWG to 6 AWG copper wire to minimize voltage drop. Always calculate the voltage drop based on the length of the wire and the current it will carry to ensure optimal performance.
What Are the Safety Tips for Using a 40 Amp Wire?
When working with a 40 amp wire, safety should always be your top priority. Here are some essential tips to keep in mind:
- Always turn off the power before working on any electrical circuit.
- Use wires that are rated for the specific application and environment.
- Ensure that all connections are secure and properly insulated.
- Follow the NEC guidelines and consult a licensed electrician if you’re unsure.
- Regularly inspect wires for signs of wear, damage, or overheating.
By following these safety tips, you can prevent accidents and ensure the longevity of your electrical system.
How Can You Avoid Common Mistakes with a 40 Amp Wire Gauge?
One of the most common mistakes people make when working with a 40 amp wire gauge is using an undersized wire. This can lead to overheating, voltage drops, and even fire hazards. To avoid this, always consult the NEC guidelines or a licensed electrician to ensure that you’re using the correct wire gauge for your application.
Another mistake is neglecting to account for the length of the wire run. Longer distances require thicker wires to compensate for voltage drop. Failing to do so can result in poor performance of connected devices.
Finally, always use wires with the appropriate insulation for the environment in which they will be installed. For example, outdoor installations may require UV-resistant or moisture-proof wires to prevent damage.
Frequently Asked Questions About 40 Amp Wire Gauges
Here are some commonly asked questions about the 40 amp wire gauge:
- What is the minimum wire gauge for a 40-amp circuit? For copper wire, 8 AWG is the minimum recommended gauge, while 6 AWG is required for aluminum wire.
- Can I use a 10 AWG wire for a 40-amp circuit? No, a 10 AWG wire is rated for 30 amps and should not be used for a 40-amp circuit.
- Does wire length affect the choice of wire gauge? Yes, longer wire runs require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop.
- What type of insulation is best for outdoor use? UV-resistant or moisture-proof insulation, such as THWN or UF cable, is ideal for outdoor installations.
In conclusion, understanding the 40 amp wire gauge is essential for anyone working with electrical systems. By choosing the correct wire gauge, you can ensure the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical installations. Always consult professional guidelines and seek expert advice when in doubt to avoid costly mistakes and ensure compliance with safety standards.