Choosing the right wire size for a 10-amp circuit is essential to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with electrical codes. Whether you're working on a DIY project or planning a professional installation, understanding the correct wire gauge is critical to prevent overheating, voltage drops, and potential fire hazards. The size of the wire you choose depends on factors like the current load, the length of the wire, and the material it's made of. By the end of this guide, you'll have a clear understanding of what size wire for 10 amps is appropriate for your needs.
Electrical systems rely on properly sized wires to function safely and efficiently. Using an undersized wire for a 10-amp circuit can lead to overheating, which may damage appliances or even cause electrical fires. On the other hand, using an oversized wire might be unnecessarily expensive and impractical. To avoid these issues, it's important to know the specific requirements for your project. This article will explore everything you need to know about selecting the correct wire size for 10 amps, including material considerations, length adjustments, and safety tips.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll break down the technical aspects of wire sizing into easy-to-understand sections. You'll learn about the differences between copper and aluminum wires, how to calculate voltage drop, and what size wire for 10 amps is recommended by industry standards. By following these guidelines, you'll not only ensure the safety of your electrical system but also improve its performance and longevity. Let's dive into the details to help you make an informed decision.
Read also:Chris Bledsoe Net Worth A Comprehensive Overview Of His Financial Success
Table of Contents
- What Size Wire for 10 Amps?
- Why Does Wire Size Matter?
- How to Choose the Right Wire for 10 Amps?
- What Are the Different Wire Materials?
- How Does Wire Length Affect Size?
- What Are the Safety Tips for Wiring?
- Can You Use Undersized Wires for 10 Amps?
- What Are the Industry Standards for Wire Sizing?
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop for 10 Amps?
- Frequently Asked Questions
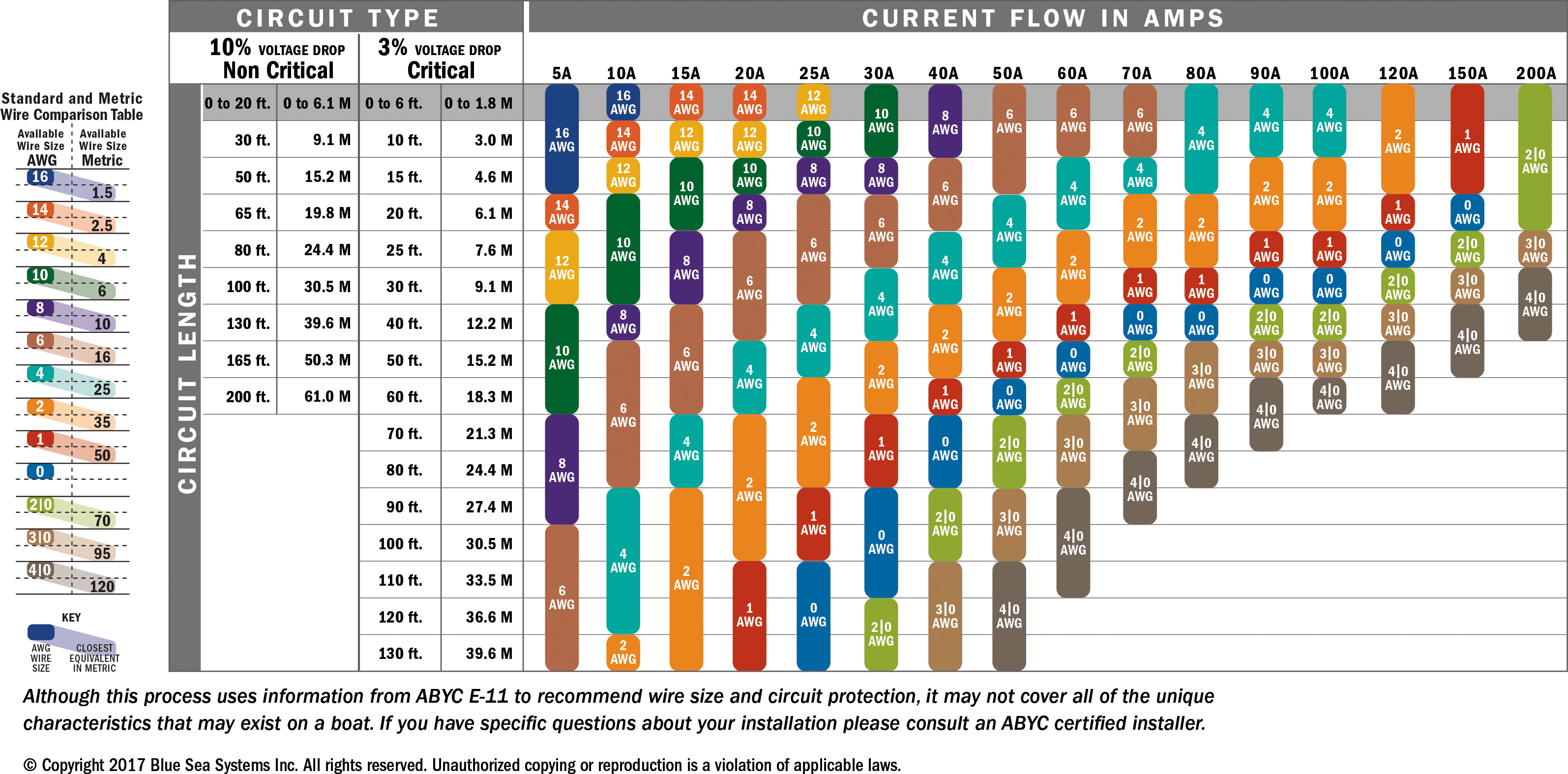
What Size Wire for 10 Amps?
For most residential and commercial applications, a 16-gauge wire is typically sufficient for a 10-amp circuit. However, this recommendation can vary based on factors such as the wire material (copper or aluminum), the length of the wire, and the specific requirements of your project. Copper wires are more conductive than aluminum, meaning they can carry the same current with a smaller diameter. If you're working with aluminum wires, you'll need to choose a slightly larger gauge to compensate for its lower conductivity.
It's also important to consider the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines, which specify the minimum wire sizes for various applications. These guidelines are designed to ensure safety and prevent electrical hazards. For example, the NEC recommends using a 14-gauge wire for 15-amp circuits, but for 10 amps, a 16-gauge wire is often sufficient. Always double-check the specific requirements for your project and consult a professional if you're unsure.
Why Does Wire Size Matter?
The size of the wire directly impacts the safety and efficiency of your electrical system. If the wire is too small for the current it needs to carry, it can overheat, leading to insulation damage or even a fire. On the other hand, using a wire that's too large can be costly and impractical without providing significant benefits. Understanding the relationship between wire size and current load is crucial for making informed decisions.
Additionally, the wire size affects voltage drop, which is the reduction in voltage as electricity travels through the wire. A significant voltage drop can cause appliances to underperform or malfunction. To minimize voltage drop, you may need to choose a larger wire, especially for longer runs. This is particularly important when determining what size wire for 10 amps is appropriate for your specific setup.
How to Choose the Right Wire for 10 Amps?
Choosing the right wire for a 10-amp circuit involves several considerations. Start by determining the material of the wire—copper or aluminum—as this will influence the gauge you need. Copper wires are more conductive and can carry the same current with a smaller diameter compared to aluminum wires. Next, consider the length of the wire. Longer wires require larger gauges to compensate for voltage drop.
Here are some key steps to guide your decision:
Read also:Unlock The Fun Infinite Craft Unblocked Ndash The Ultimate Guide
- Identify the current load: For a 10-amp circuit, a 16-gauge copper wire is typically sufficient.
- Check the wire material: Copper is preferred for its conductivity, but aluminum is also an option.
- Measure the wire length: Longer runs may require a larger gauge to prevent voltage drop.
- Consult the NEC guidelines: Ensure your choice complies with industry standards.
What Are the Different Wire Materials?
When selecting a wire for a 10-amp circuit, the material plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate size. The two most common materials are copper and aluminum. Copper is widely regarded as the superior choice due to its excellent conductivity and durability. It can carry the same current as aluminum with a smaller diameter, making it ideal for applications where space is limited.
Aluminum wires, while less expensive, are less conductive and require a larger gauge to handle the same current. They are also more prone to corrosion over time, which can affect their performance. However, aluminum is still a viable option for certain applications, especially when cost is a significant factor. Understanding the differences between these materials will help you decide what size wire for 10 amps is best for your project.
How Does Wire Length Affect Size?
The length of the wire is another critical factor when determining what size wire for 10 amps is appropriate. Longer wires experience greater resistance, which can lead to voltage drop. To compensate for this, you may need to choose a larger gauge wire to ensure the circuit functions properly. For example, a 16-gauge wire might be sufficient for a short 10-amp circuit, but a longer run might require a 14-gauge wire to maintain performance.
Here are some tips for managing wire length:
- Measure the distance between the power source and the load.
- Calculate the expected voltage drop based on the wire length and material.
- Choose a larger gauge if the voltage drop exceeds acceptable limits.
What Are the Safety Tips for Wiring?
Safety should always be your top priority when working with electrical wiring. Using the correct wire size for a 10-amp circuit is just one aspect of ensuring a safe installation. Here are some additional tips to keep in mind:
- Always turn off the power before working on electrical circuits.
- Use wire strippers to remove insulation without damaging the conductor.
- Secure connections with wire nuts or terminal blocks to prevent loose wires.
- Inspect wires regularly for signs of wear or damage.
Can You Use Undersized Wires for 10 Amps?
Using undersized wires for a 10-amp circuit is a common mistake that can lead to serious consequences. Undersized wires can overheat, causing insulation to melt and potentially starting a fire. Even if the circuit appears to function correctly, the risk of overheating increases with prolonged use. To avoid these hazards, always choose the appropriate wire size based on the current load and other factors.
What Are the Industry Standards for Wire Sizing?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for wire sizing to ensure safety and compliance. These standards specify the minimum wire sizes for various current loads and applications. For example, the NEC recommends using a 14-gauge wire for 15-amp circuits, but for 10 amps, a 16-gauge wire is often sufficient. Always refer to the NEC guidelines when determining what size wire for 10 amps is appropriate for your project.
How to Calculate Voltage Drop for 10 Amps?
Calculating voltage drop is an important step in determining the correct wire size for a 10-amp circuit. Voltage drop occurs when resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage as electricity travels through the circuit. To calculate voltage drop, you'll need to know the wire length, material, and gauge, as well as the current load.
Here's a simple formula for calculating voltage drop:
Voltage Drop = (2 x Wire Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000
Using this formula, you can determine whether your chosen wire size is sufficient or if a larger gauge is needed to maintain acceptable performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Happens if You Use the Wrong Size Wire for 10 Amps?
Using the wrong size wire for a 10-amp circuit can lead to overheating, voltage drop, and potential fire hazards. Always choose the appropriate wire size based on the current load and other factors.
Can You Use a 14-Gauge Wire for 10 Amps?
Yes, a 14-gauge wire is typically sufficient for a 10-amp circuit, especially for short runs. However, for longer distances, you may need a larger gauge to prevent voltage drop.
What Are the Best Practices for Installing Wires?
Best practices include turning off the power, using the correct tools, securing connections, and inspecting wires regularly for signs of wear or damage.
How Do You Know What Size Wire for 10 Amps is Right for Your Project?
To determine the right wire size, consider the current load, wire material, length, and industry standards. Consulting a professional is always a good idea if you're unsure.