When it comes to electrical systems, the right wire gauge is crucial for safety, efficiency, and performance. A 100 amp gauge wire is often used in applications where large amounts of current need to be carried safely. Whether you're working on a residential upgrade, an industrial setup, or a DIY project, understanding the specifications and uses of this wire type is essential. The 100 amp gauge wire is designed to handle significant electrical loads, ensuring that your system operates without overheating or causing hazards.
Selecting the correct wire gauge for your needs isn't just about meeting code requirements; it's about ensuring the longevity and reliability of your electrical system. A 100 amp gauge wire is commonly used in breaker panels, subpanels, and other high-capacity electrical setups. This type of wire is built to withstand the demands of heavy appliances, machinery, and tools, making it a popular choice for homeowners and professionals alike. Understanding its applications and limitations can save you time, money, and potential safety risks.
With the growing popularity of renewable energy systems like solar panels, the demand for 100 amp gauge wire has increased. These wires are often used to connect inverters, batteries, and other components in off-grid and hybrid setups. Their ability to transmit electricity efficiently over long distances without significant voltage drop makes them indispensable in modern electrical designs. This article will explore everything you need to know about 100 amp gauge wire, from its applications to installation tips, ensuring you're well-equipped for your next project.
Read also:Unleash The Fun A Complete Guide To Games Unblocked
- What is 100 Amp Gauge Wire?
- Why is 100 Amp Gauge Wire Important?
- How to Choose the Right 100 Amp Gauge Wire?
- Common Applications of 100 Amp Gauge Wire
- What Are the Safety Tips for Using 100 Amp Gauge Wire?
- Can You Use 100 Amp Gauge Wire for Solar Panels?
- How to Install 100 Amp Gauge Wire?
- What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid?
- How Does 100 Amp Gauge Wire Compare to Other Gauges?
- Frequently Asked Questions About 100 Amp Gauge Wire
What is 100 Amp Gauge Wire?
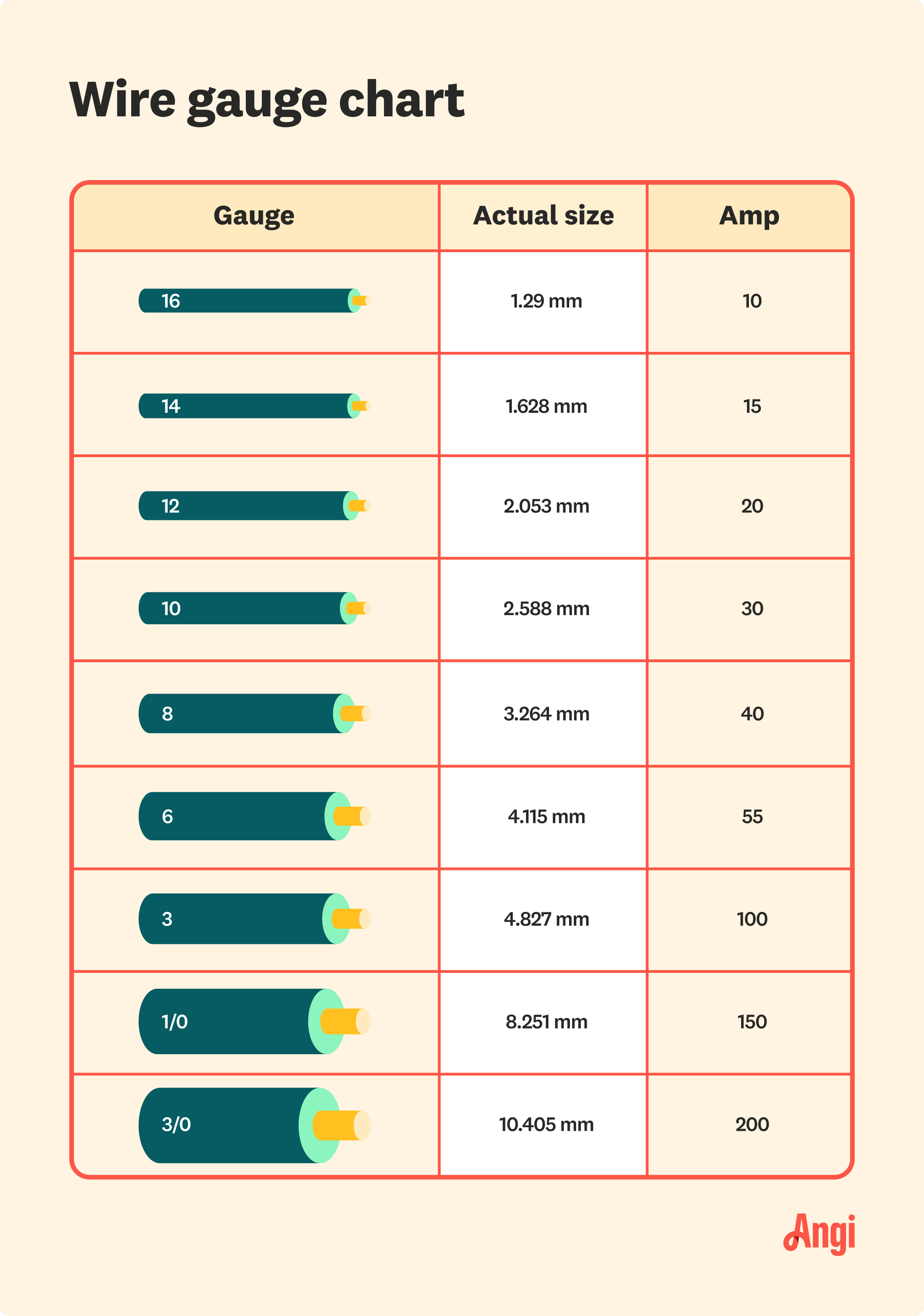
A 100 amp gauge wire is specifically designed to handle electrical currents up to 100 amps safely. These wires are typically made of copper or aluminum, with copper being the preferred material due to its superior conductivity and durability. The gauge of the wire refers to its thickness, with lower gauge numbers indicating thicker wires. For 100 amp applications, wires are usually in the range of 2 AWG to 4 AWG, depending on the material and distance of the run.
Understanding the specifications of 100 amp gauge wire is essential for ensuring compliance with electrical codes. These wires are insulated to prevent electrical leakage and are often rated for both indoor and outdoor use. The insulation material can vary, with options like PVC, THHN, and XHHW being common choices. Each type of insulation has unique properties that make it suitable for specific environments, such as moisture resistance or heat tolerance.
Why is 100 Amp Gauge Wire Important?
Using the correct wire gauge is vital for preventing overheating, electrical fires, and system failures. A 100 amp gauge wire ensures that your electrical system can handle the load without exceeding safe temperature limits. This is particularly important in applications like breaker panels, where the wire must carry a continuous current without degrading over time.
Another reason why 100 amp gauge wire is important is its role in maintaining voltage stability. When wires are too thin for the current they carry, voltage drop occurs, leading to inefficient energy use and potential damage to connected devices. By choosing the right gauge, you ensure that your system operates at optimal efficiency, reducing energy waste and costs.
How to Choose the Right 100 Amp Gauge Wire?
Selecting the appropriate 100 amp gauge wire involves considering several factors, including the material, insulation type, and length of the wire run. Here are some key considerations:
- Material: Copper is more conductive than aluminum, making it a better choice for long runs or high-load applications. However, aluminum is lighter and more cost-effective for shorter runs.
- Insulation: Choose insulation based on the environment. For example, XHHW is ideal for wet or damp locations, while THHN is suitable for dry indoor use.
- Distance: Longer runs require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop. Consult a voltage drop calculator to determine the appropriate gauge for your specific project.
Common Applications of 100 Amp Gauge Wire
A 100 amp gauge wire is versatile and can be used in a variety of settings. Some common applications include:
Read also:How To Securely Connect Remoteiot Vpc Raspberry Pi Free Download For Windows
- Residential breaker panels and subpanels
- Industrial machinery and equipment
- Solar panel systems and battery banks
- RVs and mobile homes
What Are the Safety Tips for Using 100 Amp Gauge Wire?
Working with 100 amp gauge wire requires careful attention to safety. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Always turn off the power before working on electrical systems.
- Use proper tools and equipment to avoid damaging the wire or insulation.
- Ensure that all connections are secure and free of corrosion.
Can You Use 100 Amp Gauge Wire for Solar Panels?
Yes, a 100 amp gauge wire is often used in solar panel installations. These wires are ideal for connecting inverters, charge controllers, and battery banks due to their ability to handle high currents efficiently. However, it's essential to calculate the exact requirements of your system to avoid over-sizing or under-sizing the wire.
How to Install 100 Amp Gauge Wire?
Installing 100 amp gauge wire involves several steps, including planning, measuring, and connecting. Here's a basic guide:
- Plan the wire route and measure the required length.
- Select the appropriate wire gauge and insulation type.
- Secure the wire using clamps or conduit to prevent damage.
What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid?
When working with 100 amp gauge wire, avoid these common mistakes:
- Using a wire gauge that's too thin for the load.
- Ignoring insulation requirements for specific environments.
- Failing to secure the wire properly, leading to wear and tear.
How Does 100 Amp Gauge Wire Compare to Other Gauges?
Compared to lower gauge wires, 100 amp gauge wire is thicker and can handle higher currents. For example, a 10 AWG wire is suitable for 30 amps, while a 2 AWG wire is needed for 100 amps. Choosing the right gauge ensures safety and efficiency in your electrical system.
Frequently Asked Questions About 100 Amp Gauge Wire
What is the maximum distance for 100 amp gauge wire?
The maximum distance depends on the wire gauge and material. For copper wires, a 2 AWG wire can handle up to 100 amps over 100 feet without significant voltage drop.
Can I use aluminum wire instead of copper for 100 amps?
Yes, but aluminum wires are less conductive, so you'll need a thicker gauge to achieve the same performance as copper.
How do I calculate voltage drop for 100 amp gauge wire?
Use a voltage drop calculator, inputting the wire length, gauge, and material to determine the drop.
What insulation type is best for outdoor use?
XHHW insulation is ideal for outdoor applications due to its moisture and heat resistance.
Is it safe to install 100 amp gauge wire myself?
While it's possible, it's recommended to hire a licensed electrician for safety and compliance with local codes.
In conclusion, understanding the role and applications of 100 amp gauge wire is essential for anyone working on electrical systems. By choosing the right wire, following safety guidelines, and avoiding common mistakes, you can ensure a reliable and efficient setup for your projects. Whether you're upgrading your home or installing solar panels, this wire type is a cornerstone of modern electrical design.